通过debug搞清楚.vue文件怎么变成.js文件
前言
我们每天写的
vue
代码都是写在
vue
文件中,但是浏览器却只认识
html
、
css
、
js
等文件类型。所以这个时候就需要一个工具将
vue
文件转换为浏览器能够认识的
js
文件,想必你第一时间就想到了
webpack
或者
vite
。但是
webpack
和
vite
本身是没有能力处理
vue
文件的,其实实际背后生效的是
vue-loader
和
@vitejs/plugin-vue
。本文以
@vitejs/plugin-vue
举例,通过
debug
的方式带你一步一步的搞清楚
vue
文件是如何编译为
js
文件的,
看不懂你来打我
。
举个例子
这个是我的源代码
App.vue
文件:
<template>
<h1 class="msg">{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from "vue";
const msg = ref("hello word");
</script>
<style scoped>
.msg {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
这个例子很简单,在
setup
中定义了
msg
变量,然后在
template
中将
msg
渲染出来。
下面这个是我从
network
中找到的编译后的
js
文件,已经精简过了:
import {
createElementBlock as _createElementBlock,
defineComponent as _defineComponent,
openBlock as _openBlock,
toDisplayString as _toDisplayString,
ref,
} from "/node_modules/.vite/deps/vue.js?v=23bfe016";
import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
const _sfc_main = _defineComponent({
__name: "App",
setup(__props, { expose: __expose }) {
__expose();
const msg = ref("hello word");
const __returned__ = { msg };
return __returned__;
},
});
const _hoisted_1 = { class: "msg" };
function _sfc_render(_ctx, _cache, $props, $setup, $data, $options) {
return (
_openBlock(),
_createElementBlock(
"h1",
_hoisted_1,
_toDisplayString($setup.msg),
1
/* TEXT */
)
);
}
__sfc__.render = render;
export default _sfc_main;
编译后的
js
代码中我们可以看到主要有三部分,想必你也猜到了这三部分刚好对应
vue
文件的那三块。
_sfc_main
对象的
setup
方法对应
vue
文件中的
<script setup lang="ts">
模块。_sfc_render
函数对应
vue
文件中的
<template>
模块。import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
对应
vue
文件中的
<style scoped>
模块。
debug搞清楚如何将
vue
文件编译为
js
文件
大家应该都知道,前端代码运行环境主要有两个,
node
端和浏览器端,分别对应我们熟悉的编译时和运行时。浏览器明显是不认识
vue
文件的,所以
vue
文件编译成
js
这一过程肯定不是在运行时的浏览器端。很明显这一过程是在编译时的
node
端。
要在
node
端打断点,我们需要启动一个debug 终端。这里以
vscode
举例,首先我们需要打开终端,然后点击终端中的
+
号旁边的下拉箭头,在下拉中点击
Javascript Debug Terminal
就可以启动一个
debug
终端。
假如
vue
文件编译为
js
文件是一个毛线团,那么他的线头一定是
vite.config.ts
文件中使用
@vitejs/plugin-vue
的地方。通过这个线头开始
debug
我们就能够梳理清楚完整的工作流程。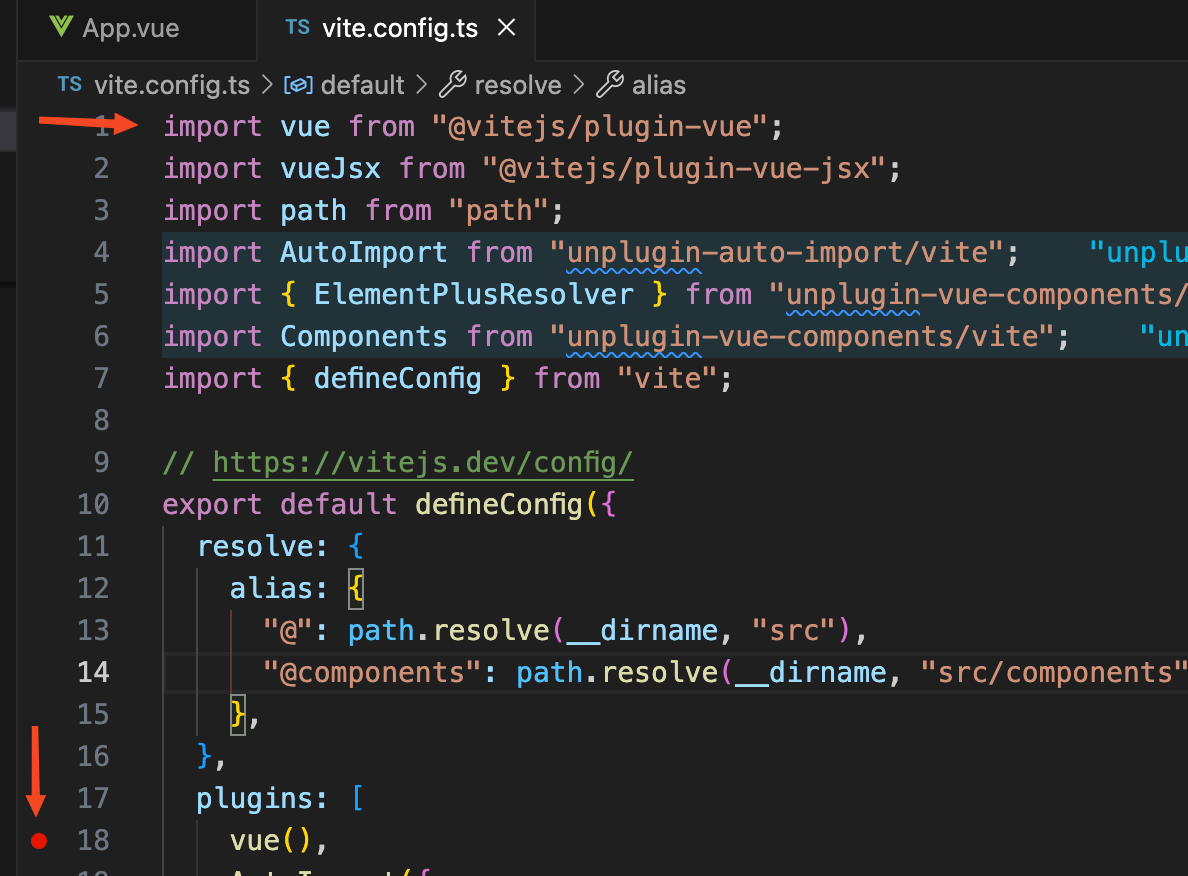
vuePlugin函数
我们给上方图片的
vue
函数打了一个断点,然后在
debug
终端上面执行
yarn dev
,我们看到断点已经停留在了
vue
函数这里。然后点击
step into
,断点走到了
@vitejs/plugin-vue
库中的一个
vuePlugin
函数中。我们看到
vuePlugin
函数中的内容代码大概是这样的:
function vuePlugin(rawOptions = {}) {
const options = shallowRef({
compiler: null,
// 省略...
});
return {
name: "vite:vue",
handleHotUpdate(ctx) {
// ...
},
config(config) {
// ..
},
configResolved(config) {
// ..
},
configureServer(server) {
// ..
},
buildStart() {
// ..
},
async resolveId(id) {
// ..
},
load(id, opt) {
// ..
},
transform(code, id, opt) {
// ..
}
};
}
@vitejs/plugin-vue
是作为一个
plugins
插件在
vite
中使用,
vuePlugin
函数返回的对象中的
buildStart
、
transform
方法就是对应的插件钩子函数。
vite
会在对应的时候调用这些插件的钩子函数,比如当
vite
服务器启动时就会调用插件里面的
buildStart
等函数,当
vite
解析每个模块时就会调用
transform
等函数。更多
vite
钩子相关内容
查看官网
。
我们这里主要看
buildStart
和
transform
两个钩子函数,分别是服务器启动时调用和解析每个模块时调用。给这两个钩子函数打上断点。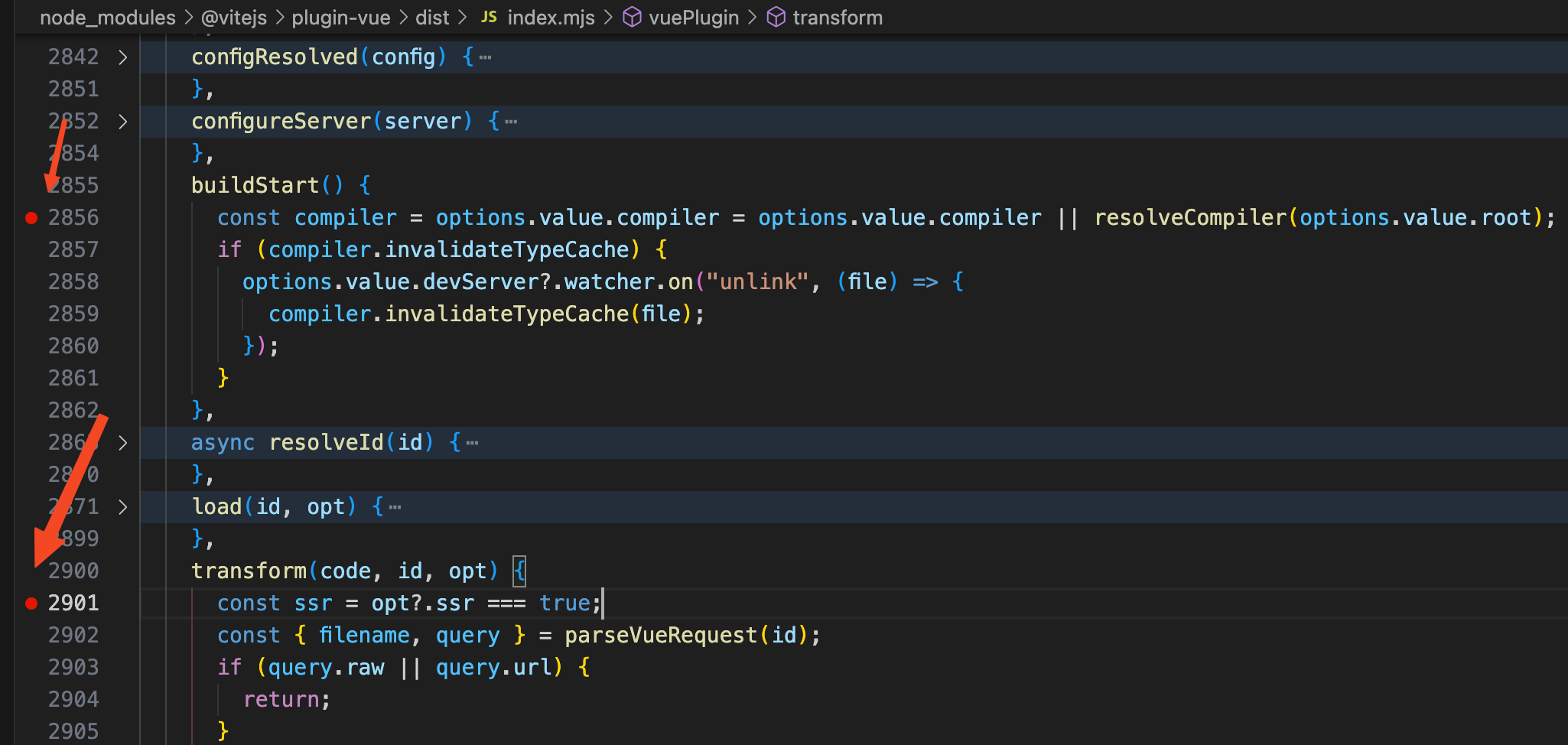
然后点击Continue(F5),
vite
服务启动后就会走到
buildStart
钩子函数中打的断点。我们可以看到
buildStart
钩子函数的代码是这样的:
buildStart() {
const compiler = options.value.compiler = options.value.compiler || resolveCompiler(options.value.root);
}
将鼠标放到
options.value.compiler
上面我们看到此时
options.value.compiler
的值为
null
,所以代码会走到
resolveCompiler
函数中,点击Step Into(F11)走到
resolveCompiler
函数中。看到
resolveCompiler
函数代码如下:
function resolveCompiler(root) {
const compiler = tryResolveCompiler(root) || tryResolveCompiler();
return compiler;
}
function tryResolveCompiler(root) {
const vueMeta = tryRequire("vue/package.json", root);
if (vueMeta && vueMeta.version.split(".")[0] >= 3) {
return tryRequire("vue/compiler-sfc", root);
}
}
在
resolveCompiler
函数中调用了
tryResolveCompiler
函数,在
tryResolveCompiler
函数中判断当前项目是否是
vue3.x
版本,然后将
vue/compiler-sfc
包返回。
所以经过初始化后
options.value.compiler
的值就是
vue
的底层库
vue/compiler-sfc
,记住这个后面会用
。
然后点击Continue(F5)放掉断点,在浏览器中打开对应的页面,比如:
http://localhost:5173/
。此时
vite
将会编译这个页面要用到的所有文件,就会走到
transform
钩子函数断点中了。由于解析每个文件都会走到
transform
钩子函数中,但是我们只关注
App.vue
文件是如何解析的,所以为了方便我们直接在
transform
函数中添加了下面这段代码,并且删掉了原来在
transform
钩子函数中打的断点,这样就只有解析到
App.vue
文件的时候才会走到断点中去。
经过debug我们发现解析
App.vue
文件时
transform
函数实际就是执行了
transformMain
函数,至于
transformStyle
函数后面讲解析
style
的时候会讲:
transform(code, id, opt) {
const { filename, query } = parseVueRequest(id);
if (!query.vue) {
return transformMain(
code,
filename,
options.value,
this,
ssr,
customElementFilter.value(filename)
);
} else {
const descriptor = query.src ? getSrcDescriptor(filename, query) || getTempSrcDescriptor(filename, query) : getDescriptor(filename, options.value);
if (query.type === "style") {
return transformStyle(
code,
descriptor,
Number(query.index || 0),
options.value,
this,
filename
);
}
}
}
transformMain
函数
继续debug断点走进
transformMain
函数,发现
transformMain
函数中代码逻辑很清晰。按照顺序分别是:
- 根据源代码code字符串调用
createDescriptor
函数生成一个
descriptor
对象。 - 调用
genScriptCode
函数传入第一步生成的
descriptor
对象将
<script setup>
模块编译为浏览器可执行的
js
代码。 - 调用
genTemplateCode
函数传入第一步生成的
descriptor
对象将
<template>
模块编译为
render
函数。 - 调用
genStyleCode
函数传入第一步生成的
descriptor
对象将
<style scoped>
模块编译为类似这样的
import
语句,
import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
。
createDescriptor
函数
我们先来看看
createDescriptor
函数,将断点走到
createDescriptor(filename, code, options)
这一行代码,可以看到传入的
filename
就是
App.vue
的文件路径,
code
就是
App.vue
中我们写的源代码。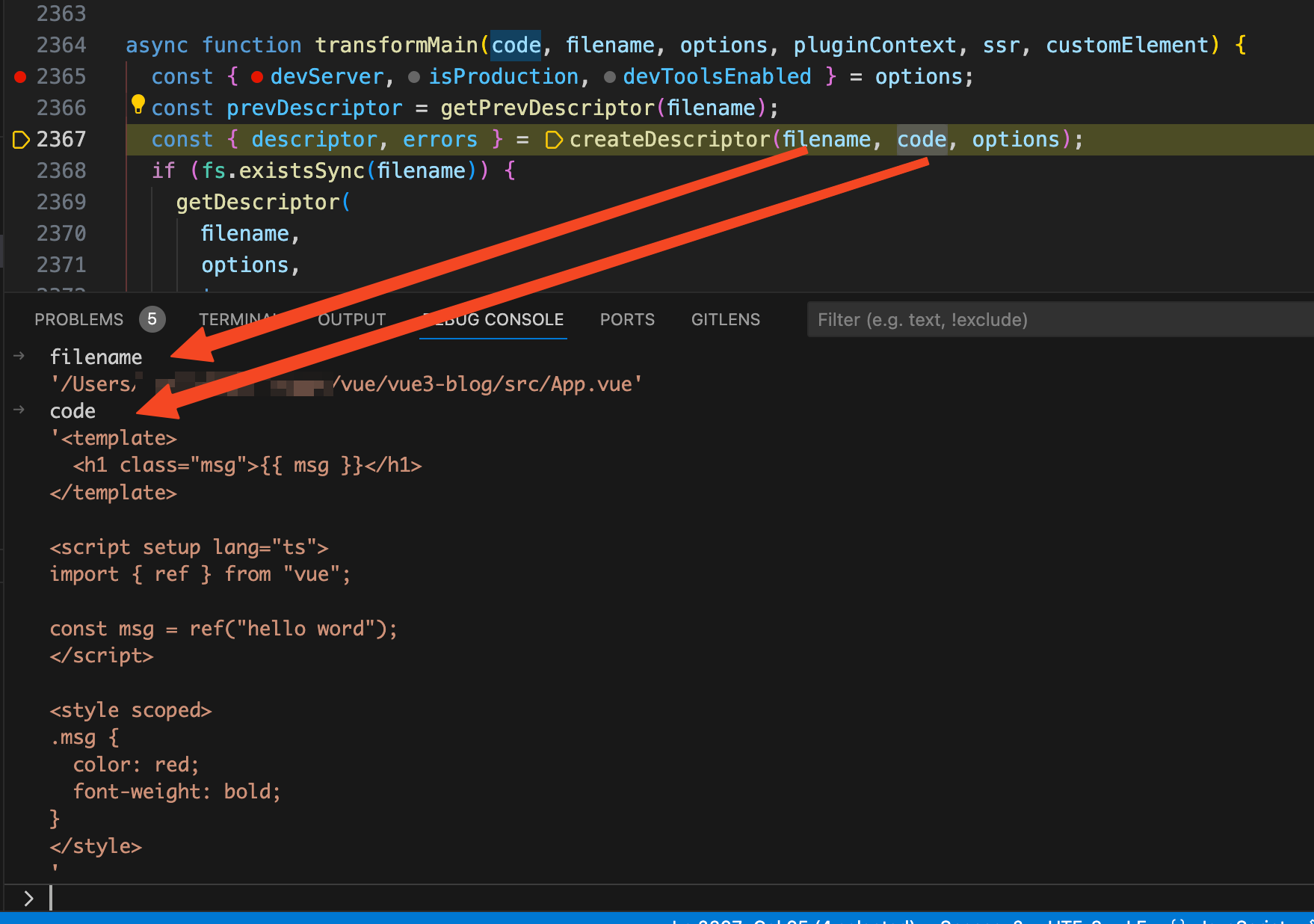
debug
走进
createDescriptor
函数,看到
createDescriptor
函数的代码如下:
function createDescriptor(filename, source, { root, isProduction, sourceMap, compiler, template }, hmr = false) {
const { descriptor, errors } = compiler.parse(source, {
filename,
sourceMap,
templateParseOptions: template?.compilerOptions
});
const normalizedPath = slash(path.normalize(path.relative(root, filename)));
descriptor.id = getHash(normalizedPath + (isProduction ? source : ""));
return { descriptor, errors };
}
这个
compiler
是不是觉得有点熟悉?
compiler
是调用
createDescriptor
函数时传入的第三个参数解构而来,而第三个参数就是
options
。还记得我们之前在
vite
启动时调用了
buildStart
钩子函数,然后将
vue
底层包
vue/compiler-sfc
赋值给
options
的
compiler
属性。那这里的
compiler.parse
其实就是调用的
vue/compiler-sfc
包暴露出来的
parse
函数,这是一个
vue
暴露出来的底层的
API
,这篇文章我们不会对底层API进行源码解析,通过查看
parse
函数的输入和输出基本就可以搞清楚
parse
函数的作用。下面这个是
parse
函数的类型定义:
export function parse(
source: string,
options: SFCParseOptions = {},
): SFCParseResult {}
从上面我们可以看到
parse
函数接收两个参数,第一个参数为
vue
文件的源代码,在我们这里就是
App.vue
中的
code
字符串,第二个参数是一些
options
选项。
我们再来看看
parse
函数的返回值
SFCParseResult
,主要有类型为
SFCDescriptor
的
descriptor
属性需要关注。
export interface SFCParseResult {
descriptor: SFCDescriptor
errors: (CompilerError | SyntaxError)[]
}
export interface SFCDescriptor {
filename: string
source: string
template: SFCTemplateBlock | null
script: SFCScriptBlock | null
scriptSetup: SFCScriptBlock | null
styles: SFCStyleBlock[]
customBlocks: SFCBlock[]
cssVars: string[]
slotted: boolean
shouldForceReload: (prevImports: Record<string, ImportBinding>) => boolean
}
仔细看看
SFCDescriptor
类型,其中的
template
属性就是
App.vue
文件对应的
template
标签中的内容,里面包含了由
App.vue
文件中的
template
模块编译成的
AST抽象语法树
和原始的
template
中的代码。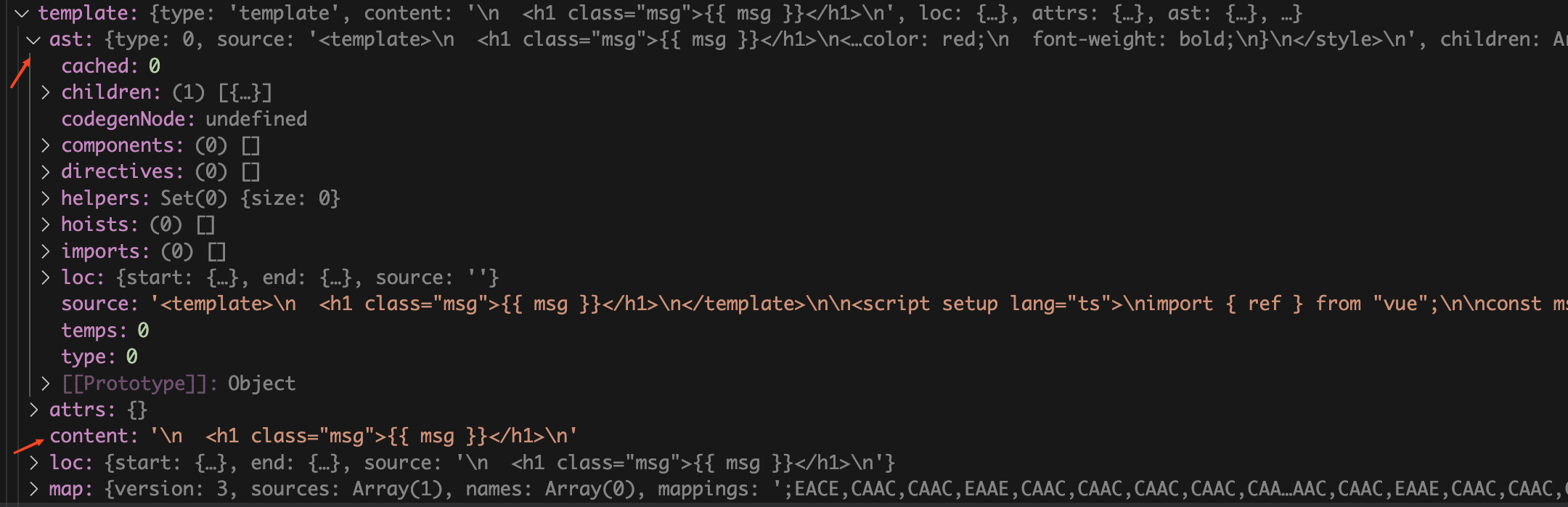
我们再来看
script
和
scriptSetup
属性,由于
vue
文件中可以写多个
script
标签,
scriptSetup
对应的就是有
setup
的
script
标签,
script
对应的就是没有
setup
对应的
script
标签。我们这个场景中只有
scriptSetup
属性,里面同样包含了
App.vue
中的
script
模块中的内容。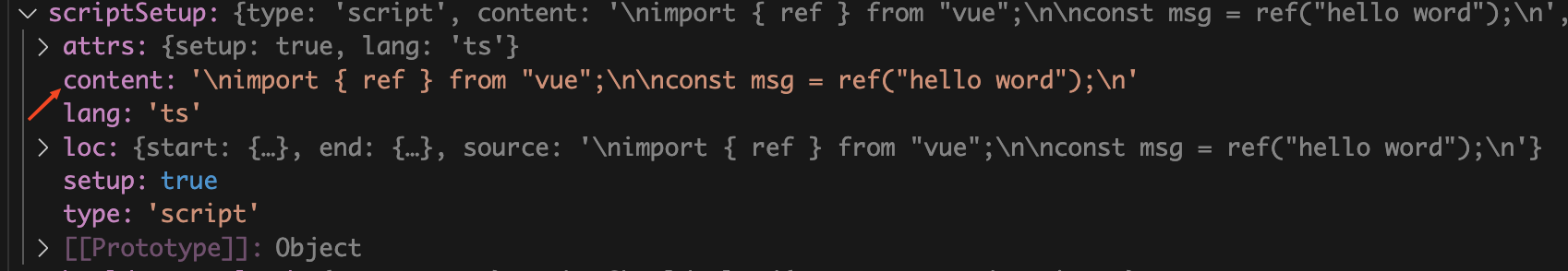
我们再来看看
styles
属性,这里的
styles
属性是一个数组,是因为我们可以在
vue
文件中写多个
style
模块,里面同样包含了
App.vue
中的
style
模块中的内容。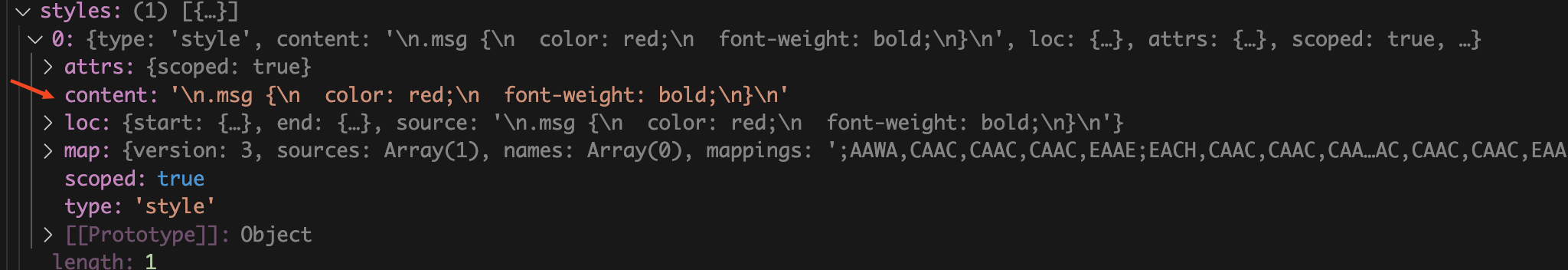
所以这一步执行
createDescriptor
函数生成的
descriptor
对象中主要有三个属性,
template
属性包含了
App.vue
文件中的
template
模块
code
字符串和
AST抽象语法树
,
scriptSetup
属性包含了
App.vue
文件中的
<script setup>
模块的
code
字符串,
styles
属性包含了
App.vue
文件中
<style>
模块中的
code
字符串。
createDescriptor
函数的执行流程图如下:
genScriptCode
函数
我们再来看
genScriptCode
函数是如何将
<script setup>
模块编译成可执行的
js
代码,同样将断点走到调用
genScriptCode
函数的地方,
genScriptCode
函数主要接收我们上一步生成的
descriptor
对象,调用
genScriptCode
函数后会将编译后的
script
模块代码赋值给
scriptCode
变量。
const { code: scriptCode, map: scriptMap } = await genScriptCode(
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
);
将断点走到
genScriptCode
函数内部,在
genScriptCode
函数中主要就是这行代码:
const script = resolveScript(descriptor, options, ssr, customElement);
。将第一步生成的
descriptor
对象作为参数传给
resolveScript
函数,返回值就是编译后的
js
代码,
genScriptCode
函数的代码简化后如下:
async function genScriptCode(descriptor, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
let scriptCode = `const ${scriptIdentifier} = {}`;
const script = resolveScript(descriptor, options, ssr, customElement);
if (script) {
scriptCode = script.content;
map = script.map;
}
return {
code: scriptCode,
map
};
}
我们继续将断点走到
resolveScript
函数内部,发现
resolveScript
中的代码其实也很简单,简化后的代码如下:
function resolveScript(descriptor, options, ssr, customElement) {
let resolved = null;
resolved = options.compiler.compileScript(descriptor, {
...options.script,
id: descriptor.id,
isProd: options.isProduction,
inlineTemplate: isUseInlineTemplate(descriptor, !options.devServer),
templateOptions: resolveTemplateCompilerOptions(descriptor, options, ssr),
sourceMap: options.sourceMap,
genDefaultAs: canInlineMain(descriptor, options) ? scriptIdentifier : void 0,
customElement
});
return resolved;
}
这里的
options.compiler
我们前面第一步的时候已经解释过了,
options.compiler
对象实际就是
vue
底层包
vue/compiler-sfc
暴露的对象,这里的
options.compiler.compileScript()
其实就是调用的
vue/compiler-sfc
包暴露出来的
compileScript
函数,同样也是一个
vue
暴露出来的底层的
API
,后面我们的分析
defineOptions
等文章时会去深入分析
compileScript
函数,这篇文章我们不会去读
compileScript
函数的源码。通过查看
compileScript
函数的输入和输出基本就可以搞清楚
compileScript
函数的作用。下面这个是
compileScript
函数的类型定义:
export function compileScript(
sfc: SFCDescriptor,
options: SFCScriptCompileOptions,
): SFCScriptBlock{}
这个函数的入参是一个
SFCDescriptor
对象,就是我们第一步调用生成
createDescriptor
函数生成的
descriptor
对象,第二个参数是一些
options
选项。我们再来看返回值
SFCScriptBlock
类型:
export interface SFCScriptBlock extends SFCBlock {
type: 'script'
setup?: string | boolean
bindings?: BindingMetadata
imports?: Record<string, ImportBinding>
scriptAst?: import('@babel/types').Statement[]
scriptSetupAst?: import('@babel/types').Statement[]
warnings?: string[]
/**
* Fully resolved dependency file paths (unix slashes) with imported types
* used in macros, used for HMR cache busting in @vitejs/plugin-vue and
* vue-loader.
*/
deps?: string[]
}
export interface SFCBlock {
type: string
content: string
attrs: Record<string, string | true>
loc: SourceLocation
map?: RawSourceMap
lang?: string
src?: string
}
返回值类型中主要有
scriptAst
、
scriptSetupAst
、
content
这三个属性,
scriptAst
为编译不带
setup
属性的
script
标签生成的AST抽象语法树。
scriptSetupAst
为编译带
setup
属性的
script
标签生成的AST抽象语法树,
content
为
vue
文件中的
script
模块编译后生成的浏览器可执行的
js
代码。下面这个是执行
vue/compiler-sfc
的
compileScript
函数返回结果: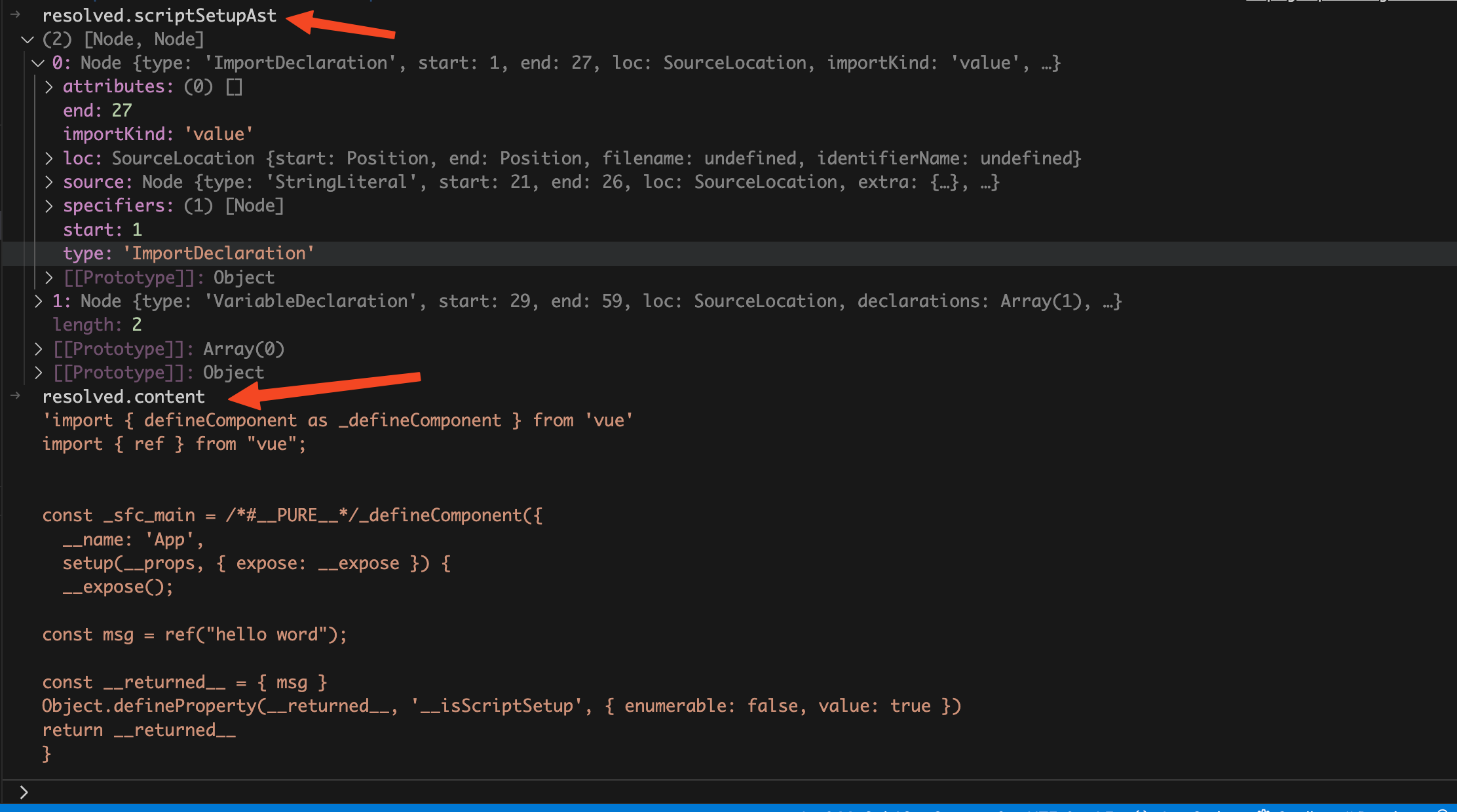
继续将断点走回
genScriptCode
函数,现在逻辑就很清晰了。这里的
script
对象就是调用
vue/compiler-sfc
的
compileScript
函数返回对象,
scriptCode
就是
script
对象的
content
属性 ,也就是将
vue
文件中的
script
模块经过编译后生成浏览器可直接执行的
js
代码
code
字符串。
async function genScriptCode(descriptor, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
let scriptCode = `const ${scriptIdentifier} = {}`;
const script = resolveScript(descriptor, options, ssr, customElement);
if (script) {
scriptCode = script.content;
map = script.map;
}
return {
code: scriptCode,
map
};
}
genScriptCode
函数的执行流程图如下: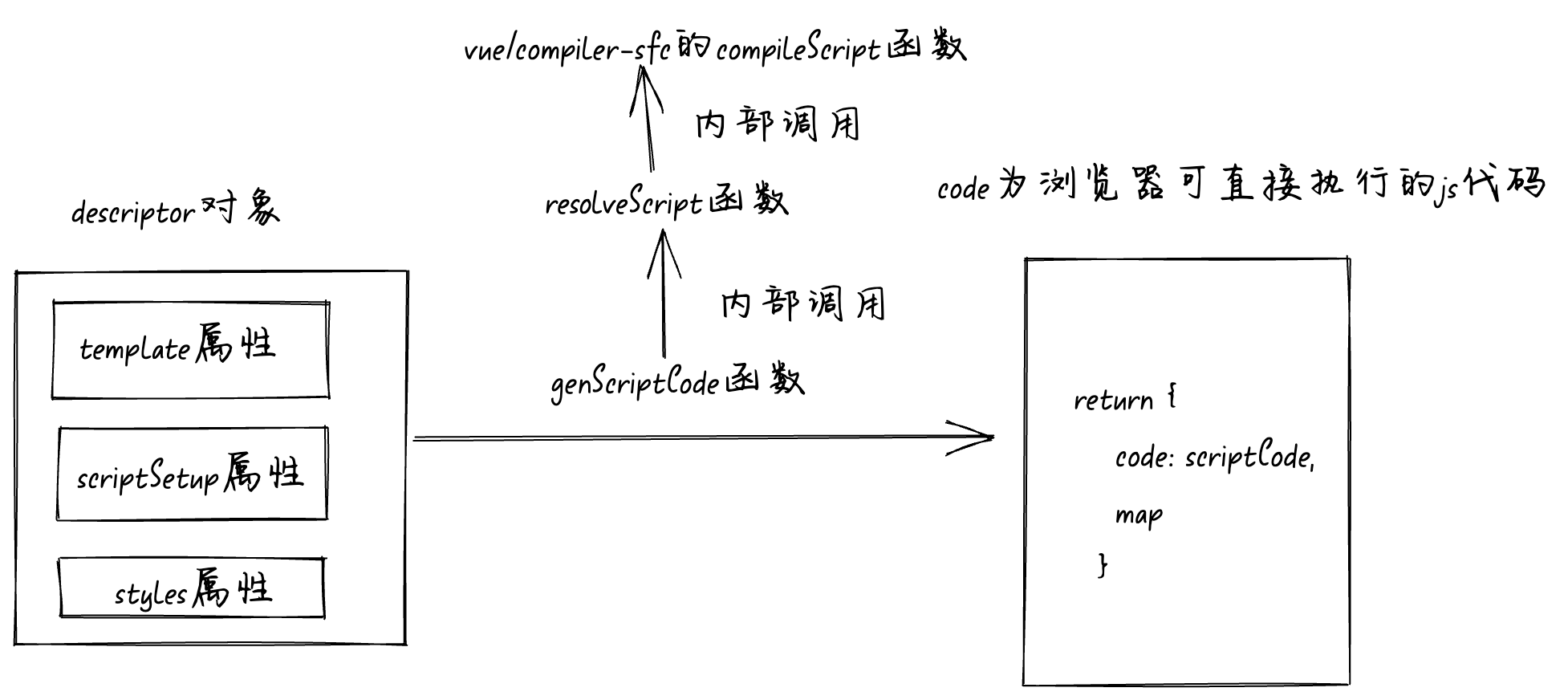
genTemplateCode
函数
我们再来看
genTemplateCode
函数是如何将
template
模块编译成
render
函数的,同样将断点走到调用
genTemplateCode
函数的地方,
genTemplateCode
函数主要接收我们上一步生成的
descriptor
对象,调用
genTemplateCode
函数后会将编译后的
template
模块代码赋值给
templateCode
变量。
({ code: templateCode, map: templateMap } = await genTemplateCode(
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
))
同样将断点走到
genTemplateCode
函数内部,在
genTemplateCode
函数中主要就是返回
transformTemplateInMain
函数的返回值,
genTemplateCode
函数的代码简化后如下:
async function genTemplateCode(descriptor, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
const template = descriptor.template;
return transformTemplateInMain(
template.content,
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
);
}
我们继续将断点走进
transformTemplateInMain
函数,发现这里也主要是调用
compile
函数,代码如下:
function transformTemplateInMain(code, descriptor, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
const result = compile(
code,
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
);
return {
...result,
code: result.code.replace(
/\nexport (function|const) (render|ssrRender)/,
"\n$1 _sfc_$2"
)
};
}
同理将断点走进到
compile
函数内部,我们看到
compile
函数的代码是下面这样的:
function compile(code, descriptor, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
const result = options.compiler.compileTemplate({
...resolveTemplateCompilerOptions(descriptor, options, ssr),
source: code
});
return result;
}
同样这里也用到了
options.compiler
,调用
options.compiler.compileTemplate()
其实就是调用的
vue/compiler-sfc
包暴露出来的
compileTemplate
函数,这也是一个
vue
暴露出来的底层的
API
。不过这里和前面不同的是
compileTemplate
接收的不是
descriptor
对象,而是一个
SFCTemplateCompileOptions
类型的对象,所以这里需要调用
resolveTemplateCompilerOptions
函数将参数转换成
SFCTemplateCompileOptions
类型的对象。这篇文章我们不会对底层API进行解析。通过查看
compileTemplate
函数的输入和输出基本就可以搞清楚
compileTemplate
函数的作用。下面这个是
compileTemplate
函数的类型定义:
export function compileTemplate(
options: SFCTemplateCompileOptions,
): SFCTemplateCompileResults {}
入参
options
主要就是需要编译的
template
中的源代码和对应的
AST抽象语法树
。我们来看看返回值
SFCTemplateCompileResults
,这里面的
code
就是编译后的
render
函数字符串。
export interface SFCTemplateCompileResults {
code: string
ast?: RootNode
preamble?: string
source: string
tips: string[]
errors: (string | CompilerError)[]
map?: RawSourceMap
}
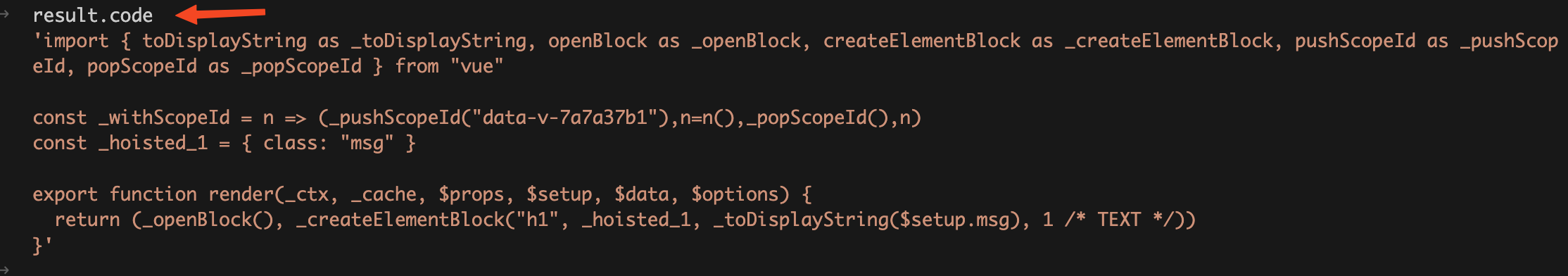
genTemplateCode
函数的执行流程图如下: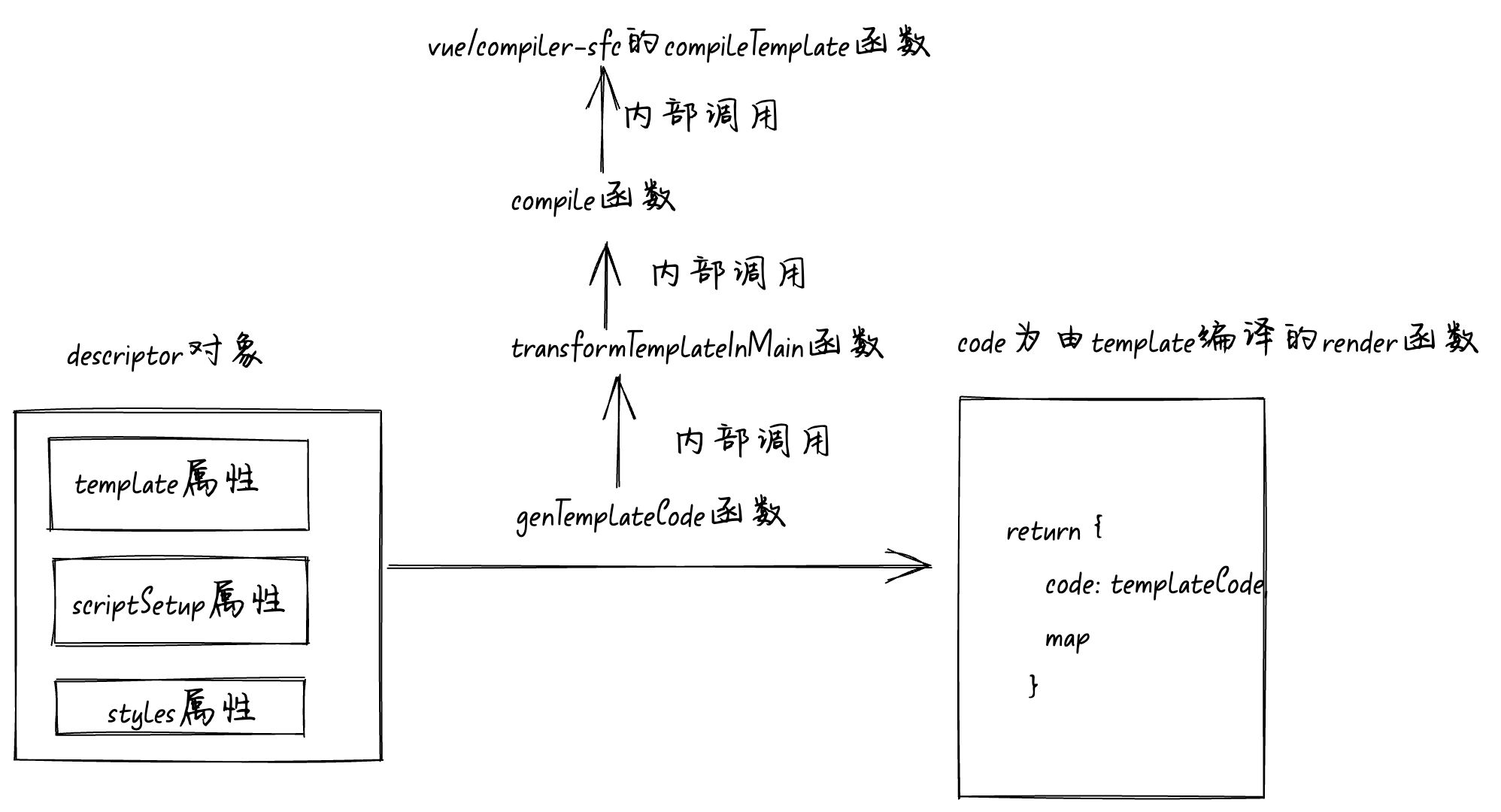
genStyleCode
函数
我们再来看最后一个
genStyleCode
函数,同样将断点走到调用
genStyleCode
的地方。一样的接收
descriptor
对象。代码如下:
const stylesCode = await genStyleCode(
descriptor,
pluginContext,
customElement,
attachedProps
);
我们将断点走进
genStyleCode
函数内部,发现和前面
genScriptCode
和
genTemplateCode
函数有点不一样,下面这个是我简化后的
genStyleCode
函数代码:
async function genStyleCode(descriptor, pluginContext, customElement, attachedProps) {
let stylesCode = ``;
if (descriptor.styles.length) {
for (let i = 0; i < descriptor.styles.length; i++) {
const style = descriptor.styles[i];
const src = style.src || descriptor.filename;
const attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(style.attrs, "css");
const srcQuery = style.src ? style.scoped ? `&src=${descriptor.id}` : "&src=true" : "";
const directQuery = customElement ? `&inline` : ``;
const scopedQuery = style.scoped ? `&scoped=${descriptor.id}` : ``;
const query = `?vue&type=style&index=${i}${srcQuery}${directQuery}${scopedQuery}`;
const styleRequest = src + query + attrsQuery;
stylesCode += `
import ${JSON.stringify(styleRequest)}`;
}
}
return stylesCode;
}
我们前面讲过因为
vue
文件中可能会有多个
style
标签,所以
descriptor
对象的
styles
属性是一个数组。遍历
descriptor.styles
数组,我们发现
for
循环内全部都是一堆赋值操作,没有调用
vue/compiler-sfc
包暴露出来的任何
API
。将断点走到
return stylesCode;
,看看
stylesCode
到底是什么东西?
通过打印我们发现
stylesCode
竟然变成了一条
import
语句,并且
import
的还是当前
App.vue
文件,只是多了几个
query
分别是:
vue
、
type
、
index
、
scoped
、
lang
。再来回忆一下前面讲的
@vitejs/plugin-vue
的
transform
钩子函数,当
vite
解析每个模块时就会调用
transform
等函数。所以当代码运行到这行
import
语句的时候会再次走到
transform
钩子函数中。我们再来看看
transform
钩子函数的代码:
transform(code, id, opt) {
const { filename, query } = parseVueRequest(id);
if (!query.vue) {
// 省略
} else {
const descriptor = query.src ? getSrcDescriptor(filename, query) || getTempSrcDescriptor(filename, query) : getDescriptor(filename, options.value);
if (query.type === "style") {
return transformStyle(
code,
descriptor,
Number(query.index || 0),
options.value,
this,
filename
);
}
}
}
当
query
中有
vue
字段,并且
query
中
type
字段值为
style
时就会执行
transformStyle
函数,我们给
transformStyle
函数打个断点。当执行上面那条
import
语句时就会走到断点中,我们进到
transformStyle
中看看。
async function transformStyle(code, descriptor, index, options, pluginContext, filename) {
const block = descriptor.styles[index];
const result = await options.compiler.compileStyleAsync({
...options.style,
filename: descriptor.filename,
id: `data-v-${descriptor.id}`,
isProd: options.isProduction,
source: code,
scoped: block.scoped,
...options.cssDevSourcemap ? {
postcssOptions: {
map: {
from: filename,
inline: false,
annotation: false
}
}
} : {}
});
return {
code: result.code,
map
};
}
transformStyle
函数的实现我们看着就很熟悉了,和前面处理
template
和
script
一样都是调用的
vue/compiler-sfc
包暴露出来的
compileStyleAsync
函数,这也是一个
vue
暴露出来的底层的
API
。同样我们不会对底层API进行解析。通过查看
compileStyleAsync
函数的输入和输出基本就可以搞清楚
compileStyleAsync
函数的作用。
export function compileStyleAsync(
options: SFCAsyncStyleCompileOptions,
): Promise<SFCStyleCompileResults> {}
我们先来看看
SFCAsyncStyleCompileOptions
入参:
interface SFCAsyncStyleCompileOptions extends SFCStyleCompileOptions {
isAsync?: boolean
modules?: boolean
modulesOptions?: CSSModulesOptions
}
interface SFCStyleCompileOptions {
source: string
filename: string
id: string
scoped?: boolean
trim?: boolean
isProd?: boolean
inMap?: RawSourceMap
preprocessLang?: PreprocessLang
preprocessOptions?: any
preprocessCustomRequire?: (id: string) => any
postcssOptions?: any
postcssPlugins?: any[]
map?: RawSourceMap
}
入参主要关注几个字段,
source
字段为
style
标签中的
css
原始代码。
scoped
字段为
style
标签中是否有
scoped
attribute。
id
字段为我们在观察 DOM 结构时看到的
data-v-xxxxx
。这个是
debug
时入参截图: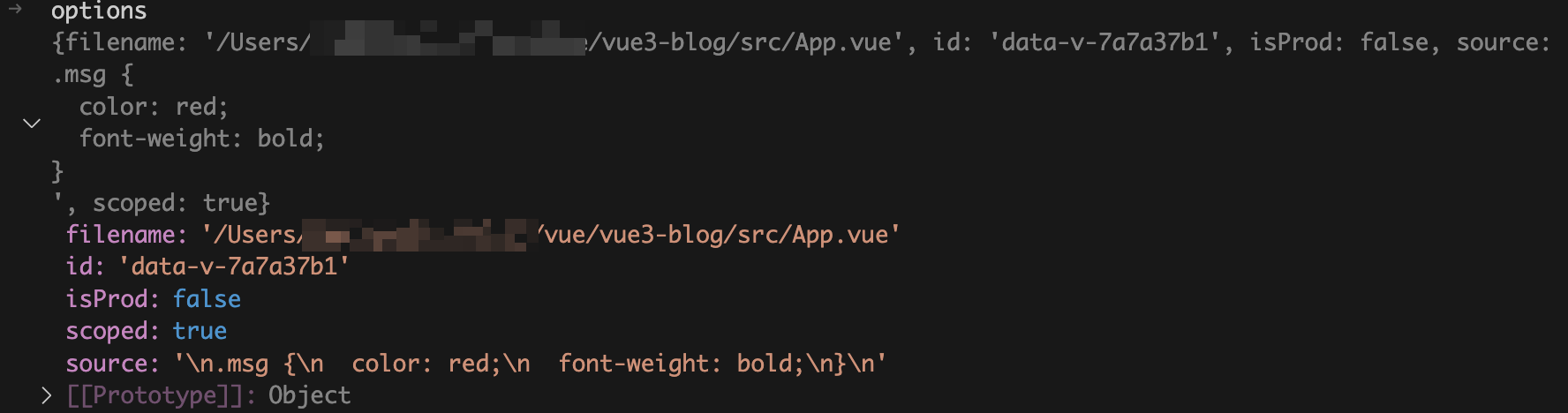
再来看看返回值
SFCStyleCompileResults
对象,主要就是
code
属性,这个是经过编译后的
css
字符串,已经加上了
data-v-xxxxx
。
interface SFCStyleCompileResults {
code: string
map: RawSourceMap | undefined
rawResult: Result | LazyResult | undefined
errors: Error[]
modules?: Record<string, string>
dependencies: Set<string>
}
这个是
debug
时
compileStyleAsync
函数返回值的截图: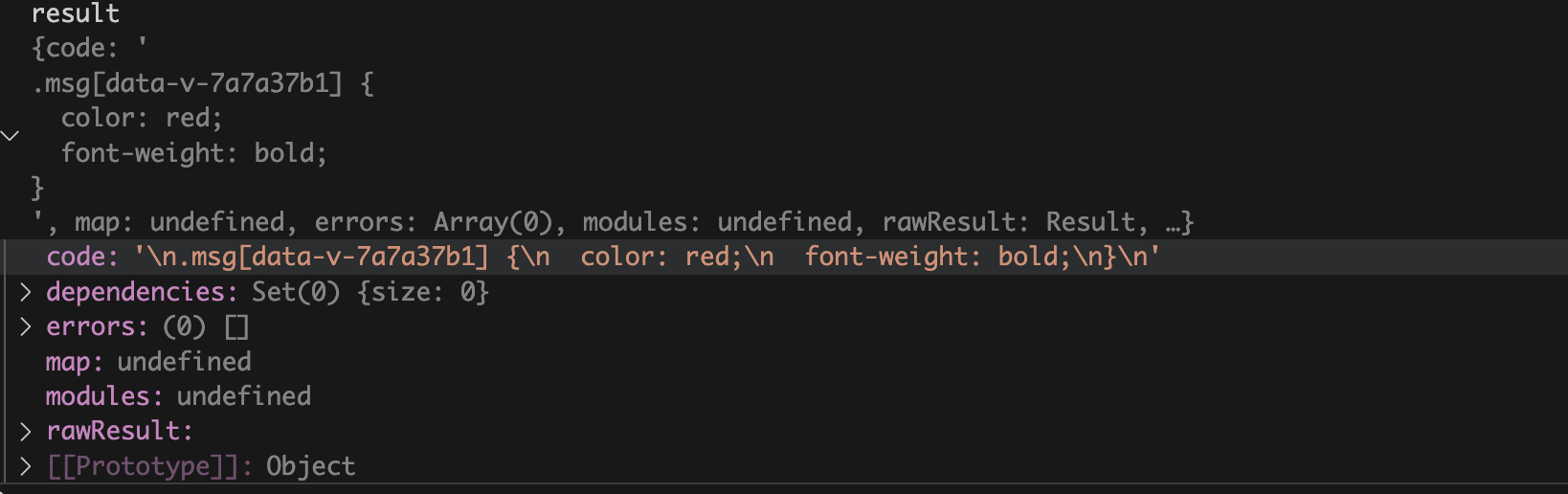
genStyleCode
函数的执行流程图如下: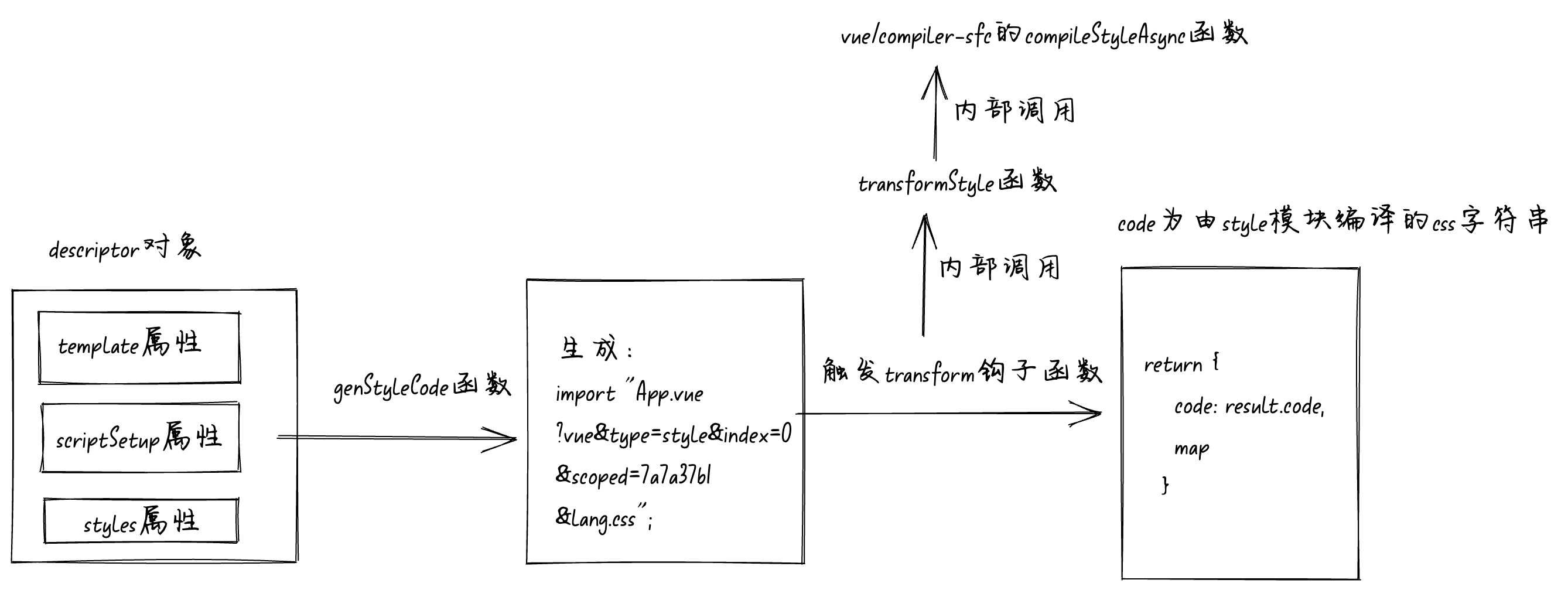
transformMain
函数简化后的代码
现在我们可以来看
transformMain
函数简化后的代码:
async function transformMain(code, filename, options, pluginContext, ssr, customElement) {
const { descriptor, errors } = createDescriptor(filename, code, options);
const { code: scriptCode, map: scriptMap } = await genScriptCode(
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
);
let templateCode = "";
({ code: templateCode, map: templateMap } = await genTemplateCode(
descriptor,
options,
pluginContext,
ssr,
customElement
));
const stylesCode = await genStyleCode(
descriptor,
pluginContext,
customElement,
attachedProps
);
const output = [
scriptCode,
templateCode,
stylesCode
];
let resolvedCode = output.join("\n");
return {
code: resolvedCode,
map: resolvedMap || {
mappings: ""
},
meta: {
vite: {
lang: descriptor.script?.lang || descriptor.scriptSetup?.lang || "js"
}
}
};
}
transformMain
函数中的代码执行主流程,其实就是对应了一个
vue
文件编译成
js
文件的流程。
首先调用
createDescriptor
函数将一个
vue
文件解析为一个
descriptor
对象。
然后以
descriptor
对象为参数调用
genScriptCode
函数,将
vue
文件中的
<script>
模块代码编译成浏览器可执行的
js
代码
code
字符串,赋值给
scriptCode
变量。
接着以
descriptor
对象为参数调用
genTemplateCode
函数,将
vue
文件中的
<template>
模块代码编译成
render
函数
code
字符串,赋值给
templateCode
变量。
然后以
descriptor
对象为参数调用
genStyleCode
函数,将
vue
文件中的
<style>
模块代码编译成了
import
语句
code
字符串,比如:
import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
,赋值给
stylesCode
变量。
然后将
scriptCode
、
templateCode
、
stylesCode
使用换行符
\n
拼接起来得到
resolvedCode
,这个
resolvedCode
就是一个
vue
文件编译成
js
文件的代码
code
字符串。这个是
debug
时
resolvedCode
变量值的截图:
总结
这篇文章通过
debug
的方式一步一步的带你了解
vue
文件编译成
js
文件的完整流程,下面是一个完整的流程图。如果文字太小看不清,可以将图片保存下来或者放大看: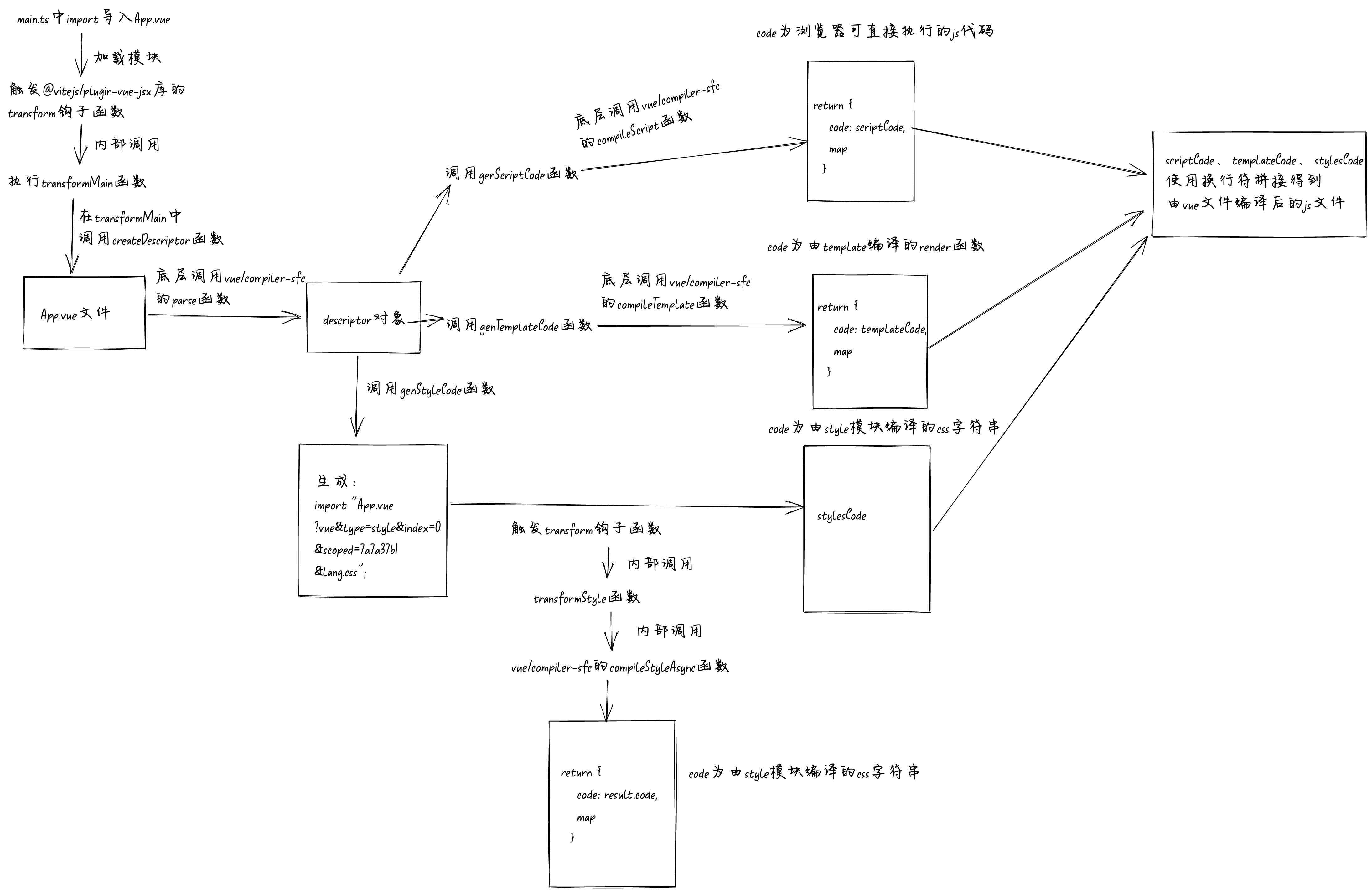
@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx
库中有个叫
transform
的钩子函数,每当
vite
加载模块的时候就会触发这个钩子函数。所以当
import
一个
vue
文件的时候,就会走到
@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx
中的
transform
钩子函数中,在
transform
钩子函数中主要调用了
transformMain
函数。
第一次解析这个
vue
文件时,在
transform
钩子函数中主要调用了
transformMain
函数。在
transformMain
函数中主要调用了4个函数,分别是:
createDescriptor
、
genScriptCode
、
genTemplateCode
、
genStyleCode
。
createDescriptor
接收的参数为当前
vue
文件代码
code
字符串,返回值为一个
descriptor
对象。对象中主要有四个属性
template
、
scriptSetup
、
script
、
styles
。
descriptor.template.ast
就是由
vue
文件中的
template
模块生成的
AST抽象语法树
。descriptor.template.content
就是
vue
文件中的
template
模块的代码字符串。scriptSetup
和
script
的区别是分别对应的是
vue
文件中有
setup
属性的
<script>
模块和无
setup
属性的
<script>
模块。
descriptor.scriptSetup.content
就是
vue
文件中的
<script setup>
模块的代码字符串。
genScriptCode
函数为底层调用
vue/compiler-sfc
的
compileScript
函数,根据第一步的
descriptor
对象将
vue
文件的
<script setup>
模块转换为浏览器可直接执行的
js
代码。
genTemplateCode
函数为底层调用
vue/compiler-sfc
的
compileTemplate
函数,根据第一步的
descriptor
对象将
vue
文件的
<template>
模块转换为
render
函数。
genStyleCode
函数为将
vue
文件的
style
模块转换为
import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
样子的
import
语句。
然后使用换行符
\n
将
genScriptCode
函数、
genTemplateCode
函数、
genStyleCode
函数的返回值拼接起来赋值给变量
resolvedCode
,这个
resolvedCode
就是
vue
文件编译成
js
文件的
code
字符串。
当浏览器执行到
import "/src/App.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&scoped=7a7a37b1&lang.css";
语句时,触发了加载模块操作,再次触发了
@vitejs/plugin-vue-jsx
中的
transform
钩子函数。此时由于有了
type=style
的
query
,所以在
transform
函数中会执行
transformStyle
函数,在
transformStyle
函数中同样也是调用
vue/compiler-sfc
的
compileStyleAsync
函数,根据第一步的
descriptor
对象将
vue
文件的
<style>
模块转换为编译后的
css
代码
code
字符串,至此编译
style
部分也讲完了。
关注公众号:
前端欧阳
,解锁我更多
vue
干货文章,并且可以免费向我咨询
vue
相关问题。