简介
开源许可: (GPL) V3
MEALPY简介
官网简介翻译
MEALPY (MEta-heuristic ALgorithms in PYthon) 是一个提供最新自然启发式元启发算法的Python模块,它是最大的此类Python模块之一。这些算法模仿自然界中的成功过程,包括生物系统以及物理和化学过程。mealPy 的目标是免费向所有人分享元启发领域的知识,帮助各领域的研究者尽快接触到优化算法,并且实现从经典到最先进的元启发算法,涵盖了元启发算法的全部历史。
MEALPY 的用途广泛,你可以使用它来分析算法参数、进行算法的定性和定量分析、分析算法的收敛速率、测试和分析算法的可扩展性和健壮性。该库目前的版本为 3.0.1,共包含 215 种算法,其中包括 190 种官方算法(原始算法、混合算法、变体算法)和 25 种开发算法。
MEALPY 的特点在于支持解决连续和离散问题,并且在新版本中,所有功能都被封装在类和对象之中,使得定义模型一次后,就可以解决多个问题。
一句话总结
MEALPY 是一个强大的
元启发式算法
Python库,它适合用于研究和解决各种优化问题,特别是对于那些复杂的
NP难题
。
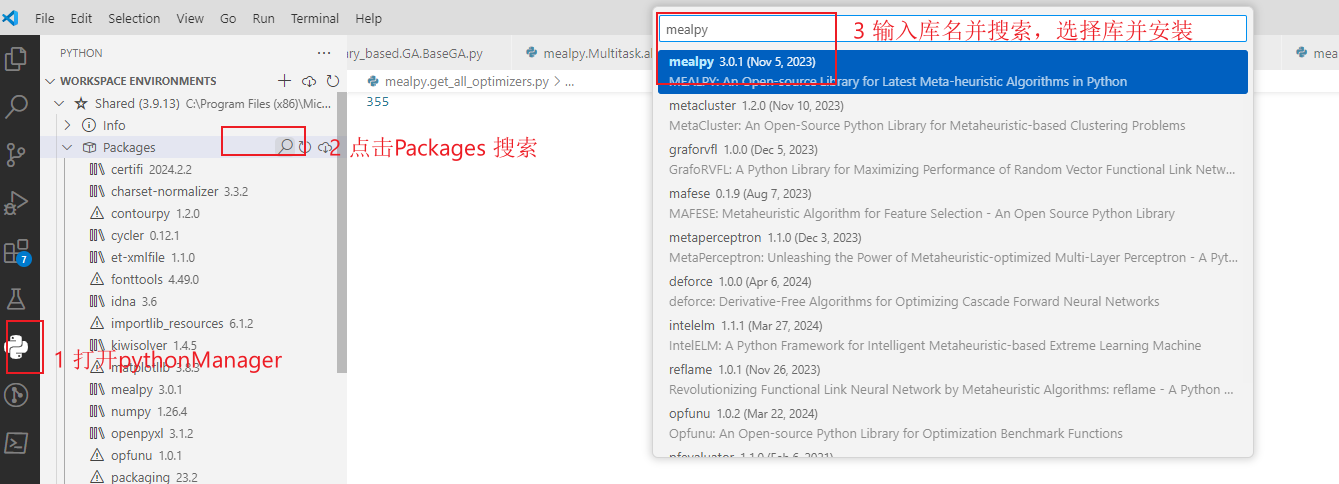
安装
安装软件和库
- python 3.7或以上
- vscode 或 pycharm (我自己用vscode)
- vscode 插件:Python Extension Pack(pycharm 忽略)
- python 库: numpy, scipy, pandas, matplotlib, mealpy( 其他遇到缺失报错的再安装也不迟)
python库直接在插件里搜就是了
基本概念
二话不说,先上一个简单代码:
from mealpy import FloatVar, GA
def objective_func(solution):
return solution**2
problem_dict = {
"obj_func": objective_func,
"bounds": FloatVar(lb=[-10000], ub=[10000]),
"minmax": "min",
}
optimizer = GA.BaseGA(epoch=100, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1)
optimizer.solve(problem_dict)
print(optimizer.g_best.solution)
print(optimizer.g_best.target.fitness)
代码解释
导入
from mealpy import FloatVar, GA
- 导入了 mealpy库里面的 FloatVar类,说明输入输出的是 float 类型的变量
- 导入了 mealpy库里面的 GA(Genetic Algorithm)遗传算法(下面解释)
定义目标函数(objective_func)
def objective_func(solution):
return solution**2
obj_func 是一个在优化问题中用来评估解决方案好坏的目标函数(objective function)。在元启发式算法中,obj_func 通常是一个接收单个解决方案(一个代表可能解的numpy向量)作为输入,并返回一个单一的实数值(在单目标优化问题中)或一个实数值列表(在多目标优化问题中)的函数。
上面objective_func 目的是找到
\(f(x)=x^2\)
,的极值(在问题字典里定义求最大还是最小值)
那么有人就会问,
\(f(x)=x^2\)
的极值不是 x=0的时候,极值也是0吗?
我想说,是的,你说的对,这不是为了举简单例子嘛(比官网例子还简单一点),如果我拿出下面公式,阁下如何应对?
\(f(x)=\sqrt[3]{x^3-x^2-x+1+y^3-xy^2}\)
所以现在我们假装不知道
\(y=x^2\)
的极值公式和图像,求一下x等于多少的时候,y的最小值。
创建问题字典(problem_dict)
problem_dict = {
"obj_func": objective_func,
"bounds": FloatVar(lb=[-10000], ub=[10000]),
"minmax": "min",
}
在mealpy库中,problem_dict 是一个字典,它定义了优化问题的所有必要信息。这个字典通常包含下列关键字:
- obj_func:这是目标函数(objective function),它接收一个候选解(通常是一个numpy数组)并返回一个评估值(对于最小化问题来说越小越好,对于最大化问题来说越大越好)。上面已经定义好了objective_func。
- bounds:这是变量的边界,它定义了解空间的上下界。在mealpy中,你可以使用不同的类型来定义边界,如FloatVar, IntVar, BoolVar等,以适应不同类型的优化问题。假设我们不知道
\(f(x)=x^2\)
的图像,但看样子,x可以取值
\((-\infty,\infty)\)
,我们程序不可能取
\((-\infty,\infty)\)
,不做特殊处理肯定会溢出,我现在就小小试一下,设
\(x \in [-10000,10000]\)
, 然后x是实数,所以bounds属于FloatVar类型,lb,ub表示上下界,是个数组,但因为我们现在的例子只有一个输入,所以[]里面只有一个边界。
- minmax:这是一个字符串,它指示优化问题是最小化问题("min")还是最大化问题("max")。我们这里是例子求
\(f(x)\)
最小值, 所以设置为min
初始化优化程序并执行 (以遗传算法为例)
optimizer = GA.BaseGA(epoch=100, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1)
optimizer.solve(problem_dict)
这段代码做了以下两件主要事情:
- 初始化遗传算法优化器。
- 使用该优化器解决定义好的优化问题。
让我们解释这段代码之前,先说一下什么是遗传算法
遗传算法(觉得太长可以跳过不看)
遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,简称GA)是计算数学中用于解决优化和搜索问题的一种启发式算法。它是由约翰·霍兰德(John Holland)在20世纪70年代初期发展起来的,其设计灵感来源于生物进化中的自然选择和遗传学原理。
遗传算法的基本概念包括个体、种群、适应度、选择、交叉(或称为杂交,英文为crossover)、变异等,以下是这些概念的详细介绍:
个体(Individual):
在遗传算法中,每一个可能的解都称为一个“个体”,通常表示为一串“基因”,这可以是二进制值、实数或其他编码形式。
我们上面例子里,因为输入只有一个,那么个体就是那个公式里的
\(x\)
浮点本身,或者是代码里目标方法(objective_func)的 solution参数本身。
种群(Population):
种群是一组个体的集合,算法从这个种群中选择个体来进行遗传操作并产生新一代种群。
我们上面例子里,
pop_size=50
就是一开始有 50个x(一般初始化,都是随机的,[-10000,10000]范围内随机生成50个x)
适应度(Fitness):
适应度是评价个体优劣的标准,它是一个函数,用于衡量个体解决问题的能力。个体的适应度越高,它被选中并遗传到下一代的机会就越大。
因为我们设置了求最小值
"minmax": "min",
,可以认为Fitness等价于例子里的 objective_func。
选择(Selection):
选择是根据个体的适应度从当前种群中选出一部分个体,用于生成下一代。常见的选择方法有轮盘赌选择、锦标赛选择, 随机选择等。
BaseGA 类通过
selection_process__
方法实现了几种不同的选择策略:
- 轮盘赌选择(Roulette Wheel Selection):使用
get_index_roulette_wheel_selection
方法,根据适应度比例选择个体。
- 随机选择(Random Selection):随机选择两个不同的个体作为父母。
- 锦标赛选择(Tournament Selection):使用
get_index_kway_tournament_selection
方法,随机选择一组个体,然后从中挑选出最好的个体。k_way 参数决定了锦标赛的大小。
BaseGA 类的初始化方法
init
允许用户设置选择策略(selection 参数),默认是
锦标赛选择
。
class BaseGA(Optimizer):
def __init__(self, epoch: int = 10000, pop_size: int = 100, pc: float = 0.95, pm: float = 0.025, **kwargs: object) -> None:
# ... 初始化代码
self.selection = "tournament"
if "selection" in kwargs:
self.selection = self.validator.check_str("selection", kwargs["selection"], ["tournament", "random", "roulette"])
# ... 初始化代码
选择策略,如果不指定 selection 参数,则会使用默认的锦标赛选择。如果你想使用轮盘赌选择或随机选择,需要在创建 BaseGA 实例时通过 selection 参数明确指定。
例子使用方式,例如:
model = BaseGA(epoch=100, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1, selection="roulette")
交叉(Crossover):
交叉是遗传算法中产生新个体的主要方式。它模拟生物学中的杂交现象,通过组合两个“父母”个体的部分基因来产生“子代”个体。
例子中 pc=0.85 表示交叉概率是 85%,意味着每一代中有 85% 的个体将通过交叉来产生新的后代。
在BaseGA类中,交叉(Crossover)是通过
crossover_process__
方法实现的。该方法定义了几种不同的交叉策略:
算术交叉(Arithmetic Crossover):通过算术运算结合两个父代的基因来产生子代。在这个实现中,可能是按照一定权重将两个父代的基因线性组合。
单点交叉(One-Point Crossover):选择一个随机的位置(切点),然后交换两个父代在这个切点位置以前和以后的基因段,从而产生两个子代。
多点交叉(Multi-Point Crossover):选择多个切点,并在这些切点位置将父代的基因段交叉组合,产生子代。
均匀交叉(Uniform Crossover):对于每个基因位点,随机决定该位置的基因是来自父代1还是父代2。这个决策是独立于其他基因位点的。
以下是
crossover_process__
方法的代码实现:
def crossover_process__(self, dad, mom):
if self.crossover == "arithmetic":
w1, w2 = self.crossover_arithmetic(dad, mom)
elif self.crossover == "one_point":
cut = self.generator.integers(1, self.problem.n_dims-1)
w1 = np.concatenate([dad[:cut], mom[cut:]])
w2 = np.concatenate([mom[:cut], dad[cut:]])
elif self.crossover == "multi_points":
idxs = self.generator.choice(range(1, self.problem.n_dims-1), 2, replace=False)
cut1, cut2 = np.min(idxs), np.max(idxs)
w1 = np.concatenate([dad[:cut1], mom[cut1:cut2], dad[cut2:]])
w2 = np.concatenate([mom[:cut1], dad[cut1:cut2], mom[cut2:]])
else: # uniform
flip = self.generator.integers(0, 2, self.problem.n_dims)
w1 = dad * flip + mom * (1 - flip)
w2 = mom * flip + dad * (1 - flip)
return w1, w2
在这个方法中,dad和mom参数表示两个父代的基因串。根据self.crossover的值,它决定使用哪种交叉策略。每种策略都会计算并返回两个子代w1和w2的基因串。
注意,实际的交叉操作是否发生是由交叉概率self.pc控制的,这个概率决定了在种群中有多少比例的个体会经历交叉过程。如果随机数小于self.pc,那么调用crossover_process__方法进行交叉;否则,子代直接继承父代的基因。
简单来说,BaseGA类中的交叉是通过拼接两个父代的某些部分来产生子代,具体的拼接方式取决于所选的交叉策略。
BaseGA默认使用均匀交叉uniform,对于浮点数的均匀交叉(Uniform Crossover),方法与处理二进制串或整数串的方式类似,但是要考虑到浮点数的连续性。在均匀交叉中,每个基因位点都有一个独立的概率决定是从父代1继承还是从父代2继承。
对于浮点数列表的均匀交叉,可以按如下方式进行:
- 对于个体中的每一个浮点数位点(在这个案例中,由于只有一个浮点数,所以只有一个位点)生成一个0到1之间的随机数。
- 如果这个随机数小于预设的阈值(通常是0.5),则从父代1中选取该位点的值;否则,从父代2中选取该位点的值。
因为在上面例子中,每个个体只包含一个浮点数,所以均匀交叉将简化为以下步骤:
- 生成一个0到1之间的随机数。
- 如果随机数小于0.5,子代将继承父代1的值;如果随机数大于或等于0.5,子代将继承父代2的值。
变异(Mutation):
变异是在个体的基因序列中随机改变某些基因的过程,这增加了种群的多样性,有助于算法跳出局部最优解,探索更广泛的搜索空间。
在BaseGA类中,变异(Mutation)是通过
mutation_process__
方法实现的。该方法根据所选的变异策略来对子代进行变异操作。变异操作的目的是在遗传算法的演化过程中引入一些随机性,以避免算法过早收敛到局部最优解,并增加搜索全局最优解的可能性。
BaseGA类提供了以下几种变异策略:
- 翻转变异(Flip Mutation):随机选择基因串中的一个或多个位点,并将其值改变。对于浮点数,这通常意味着重新生成一个在给定范围内的随机值来替换当前的基因值。
- 交换变异(Swap Mutation):随机选择基因串中的两个位点,并交换它们的值。
- 扰乱变异(Scramble Mutation):随机选择基因串中的一段序列,并将这段序列中的基因值进行随机打乱。
- 逆序变异(Inversion Mutation):随机选择基因串中的一段序列,并将这段序列中的基因值逆序排列。
在BaseGA类的mutation_process__方法中,根据变异概率self.pm来决定是否对子代进行变异操作(默认是翻转变异Flip)。以下是mutation_process__方法的代码实现(部分):
def mutation_process__(self, child):
if self.mutation_multipoints:
if self.mutation == "swap":
# ... Swap mutation logic ...
else: # "flip"
mutation_child = self.problem.generate_solution()
flag_child = self.generator.uniform(0, 1, self.problem.n_dims) < self.pm
return np.where(flag_child, mutation_child, child)
else:
if self.mutation == "swap":
# ... Swap mutation logic for single point ...
elif self.mutation == "inversion":
# ... Inversion mutation logic ...
elif self.mutation == "scramble":
# ... Scramble mutation logic ...
else: # "flip"
idx = self.generator.integers(0, self.problem.n_dims)
child[idx] = self.generator.uniform(self.problem.lb[idx], self.problem.ub[idx])
return child
在上述代码中,
self.problem.n_dims
表示个体中基因的数量。
self.problem.generate_solution()
是生成一个新的随机解,该解可能会用于替换当前子代的某些基因。
self.generator.uniform(0, 1, self.problem.n_dims)
生成一个0到1之间的随机数数组,与变异概率
self.pm
比较,确定哪些基因位点将发生变异。
np.where
函数根据这个条件选择性地替换基因值。
对于例子里单浮点数的个体,翻转变异将简化为在给定的值范围内重新生成一个随机浮点数。如果变异策略是swap、scramble或inversion,由于只有一个浮点数,这些策略将不适用或不产生任何效果。
回到例子
optimizer = GA.BaseGA(epoch=100, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1)
这行代码创建了一个遗传算法优化器的实例,并设置了几个重要的参数:
- epoch=100:这指定了算法的迭代次数,即算法将运行100代。
- pop_size=50:这指定了种群的大小,即每一代中有50个候选解。
- pc=0.85:这是交叉概率(crossover probability),指在每一代中,有多少比例的候选解将通过交叉(即基因的重组)来产生新的后代。在这里,设置为85%。
- pm=0.1:这是变异概率(mutation probability),指在每一代中,有多少比例的候选解将经历变异(即基因的随机改变)。在这里,设置为10%。
这些参数是遗传算法性能的关键,它们需要根据具体问题进行调整以达到最佳效果。
optimizer.solve(problem_dict)
这行代码调用优化器的 solve 方法,并传递之前定义的 problem_dict 作为参数。solve 方法将使用遗传算法来寻找最优解或者尽可能接近最优解的解决方案。
problem_dict 包含了目标函数 obj_func(用于评估解的质量)、解的边界 bounds(定义了解的搜索空间),以及优化目标 minmax(指明是最小化问题还是最大化问题)。
通过执行这两行代码,遗传算法将运行指定的迭代次数(在本例中为100代),并在每一代中使用遗传操作(选择、交叉、变异)来改进解,最终返回找到的最佳解。这个最佳解将是根据目标函数评估得到的最优质的解,同时受到解空间边界的约束。
打印结果
print(optimizer.g_best.solution)
print(optimizer.g_best.target.fitness)
最后,优化算法运算结束,打印最佳方案即
\(x\)
和最佳适应度,本例子等价于
\(f(x)\)
最小值。
结果如下:
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: Solving single objective optimization problem.
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 1, Current best: 509877.0525830909, Global best: 509877.0525830909, Runtime: 0.00927 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 2, Current best: 432309.9094269061, Global best: 432309.9094269061, Runtime: 0.00697 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 3, Current best: 432309.9094269061, Global best: 432309.9094269061, Runtime: 0.00829 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 4, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00681 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 5, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00785 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 6, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00749 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 7, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00863 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 8, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00734 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 9, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00702 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 10, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00653 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 11, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00696 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 12, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00776 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 13, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00768 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 14, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00854 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 15, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00748 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 16, Current best: 48716.68478834449, Global best: 48716.68478834449, Runtime: 0.00735 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 17, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00716 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 18, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00768 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 19, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00796 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 20, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00805 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 21, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00838 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 22, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00754 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 23, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00818 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 24, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00731 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 25, Current best: 17626.98464372988, Global best: 17626.98464372988, Runtime: 0.00890 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 26, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00742 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 27, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00778 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 28, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00720 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 29, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00776 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 30, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00761 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 31, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00767 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 32, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00734 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 33, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00767 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 34, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00835 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 35, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00910 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 36, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00857 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 37, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00941 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 38, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00676 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 39, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00808 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 40, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00701 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 41, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00844 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 42, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00701 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 43, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00953 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 44, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00694 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 45, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00839 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 46, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00770 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 47, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00756 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 48, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00758 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 49, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00846 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 50, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00739 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 51, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00702 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 52, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00773 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 53, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00734 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 54, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00775 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 55, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00721 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 56, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00710 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 57, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00803 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 58, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00802 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 59, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00802 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:05 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 60, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00728 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 61, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00769 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 62, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00647 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 63, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00755 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 64, Current best: 5265.4477712475245, Global best: 5265.4477712475245, Runtime: 0.00766 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 65, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00891 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 66, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00743 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 67, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00778 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 68, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00698 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 69, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00776 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 70, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00697 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 71, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00864 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 72, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00715 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 73, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00817 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 74, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00633 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 75, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00836 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 76, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00716 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 77, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00754 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 78, Current best: 2293.6227363517078, Global best: 2293.6227363517078, Runtime: 0.00699 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 79, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00819 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 80, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00794 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 81, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00770 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 82, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00727 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 83, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00771 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 84, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00749 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 85, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00729 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 86, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00784 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 87, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00805 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 88, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00724 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 89, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00733 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 90, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00749 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 91, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00745 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 92, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00724 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 93, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00797 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 94, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00968 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 95, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.01172 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 96, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.01594 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 97, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.01259 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 98, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00722 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 99, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00835 seconds
2024/04/11 11:29:06 AM, INFO, mealpy.evolutionary_based.GA.BaseGA: >>>Problem: P, Epoch: 100, Current best: 1232.002800987481, Global best: 1232.002800987481, Runtime: 0.00735 seconds
[35.09989745]
1232.002800987481
结果分析
就看结果的最后两行,不要看中间过程,中间过程可以拿来分析,如果不想看到中间过程,可以在问题字典里添加
"log_to": None,
键值对。
# 定义问题字典
problem_dict = {
"obj_func": objective_func,
"bounds": FloatVar(lb=[-10000], ub=[10000]),
"minmax": "min",
"log_to": None,
}
迭代100代,从-10000到10000 实数里,最终结果算出来,当
\(x=35.09989745\)
时,
\(f(x)\)
最小,且等于1232.002800987481
然后,第一次接触遗传算法的,不禁会发出大大的疑问:搞了半天,就这????!!!!我一秒钟都得出是
\(x=0\)
了。
我知道你困了累了,但请别困,别累。
从结果来看,那说明咱们上面说的原理没错,确实是一步一步的遗传变异,得到的结果。至于结果不如意,那肯定是需要继续调优的。不然那些调包侠,调参侠的称呼怎么来的?
参数调优分析
GA.BaseGA 它在寻找全局最优解的过程中可能会找到局部最优解或者近似解。遗传算法的性能(即能否找到全局最优解以及找到解的速度)取决于多个因素,包括:
- 目标函数的复杂性和多峰性:如果目标函数有很多局部最优解,算法可能陷入其中之一而不是全局最优解。
- 种群大小(pop_size):较大的种群可以提供更多的多样性,有助于探索解空间但同时也会增加计算成本。
- 交叉概率(pc)和变异概率(pm):这些参数控制算法的探索和开发的平衡,需要根据具体问题进行调整。
- 选择、交叉和变异操作的策略:这些操作如何实施也会影响算法的表现。
- 迭代次数(epoch):迭代次数越多,算法有更多的机会改进当前解,但同时也意味着更高的计算成本。
例子中目标函数是一个简单的单变量平方函数,它的全局最小值在 x = 0 处(假装不知道)。遗传算法应该能够找到这个全局最小值,或者至少是一个非常接近的近似值。结果不尽如人意,可能有几个原因:
- 随机性:遗传算法包含随机性,每次运行可能得到不同的结果。可能需要多次运行来获得更好的统计结果。
- 参数设置:pop_size、pc 和 pm 这些参数可能需要调整以适应特定问题。
- 初始化:初始种群的生成可能没有很好地覆盖解空间。
- 早熟收敛:算法可能过早地收敛到了一个局部最优解而非全局最优解。
- 迭代次数(epoch)不足:可能需要更多的迭代次数来允许算法有足够的时间来优化解。
要改进结果,可以尝试以下方法:
- 增加迭代次数:增加epoch的值,允许算法有更多的时间来改进解。
- 调整初始种群的生成。
- 调整种群大小:增加pop_size的值,提供更多的初始解和多样性。
- 调整交叉和变异概率:调整pc和pm的值,尝试找到更好的探索和开发之间的平衡。
- 多次运行:由于遗传算法的随机性质,多次运行并取最佳结果可能有助于获得更好的解。
优化
根据上面的分析,我们可以挑一两个参数试试
优化1: 大力出奇迹,增加迭代次数
代码其他不变,代数从100 代变成 10000代
optimizer = GA.BaseGA(epoch=10000, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1)
结果:
[-0.20769044]
0.04313531784135752
看来结果是-0.2,还是不太能接受,继续努力优化。
优化2 : 启用先知预测功能,边界值调小
从结果来看,
\(x\)
越来越小,那么,
\(x\)
边界值就可以不用从[-10000,10000]这么大范围筛选了,直接[-10,10]
problem_dict = {
"obj_func": objective_func,
"bounds": FloatVar(lb=[-10], ub=[10]),
"minmax": "min", }
optimizer = GA.BaseGA(epoch=10000, pop_size=50, pc=0.85, pm=0.1)
结果:
[7.35480744e-05]
5.409319244888902e-09
$x= 7.35480744 \times 10^{-5}, f(x)= 5.409319244888902 \times 10^{-9} $
第二次结果看起来非常不错。运气不错哈。(不要脸!)
总结
这只是我对mealpy库的入门尝试,还有很多高级特性没用上,比如多线程,微调,画图等等,优化算法也只是研究了BaseGA,其他算法估计也有其独到之处。
举的例子也是非常没有实际应用的可能性。
在这些探索留到日后有空再慢慢看看吧,这篇主要目的是让大家知道有这么一个库。
我也是零基础入门中,文章中可能有些错误,欢迎指正。