【SpringBootStarter】自定义全局加解密组件
【SpringBootStarter】
目的
- 了解
SpringBoot Starter
相关概念以及开发流程 - 实现自定义
SpringBoot Starter
(全局加解密) - 了解测试流程
- 优化
最终引用的效果:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xbhog</groupId>
<artifactId>globalValidation-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
了解SpringBoot Starter相关概念以及开发流程
SpringBoot Starter
SpringBoot Starter
作用将一组相关的依赖打包,简化项目的配置和初始化过程,通过特定的
Starter
开发者可以快速的实现特定功能模块的开发和扩展。
自定义
Starter
能够促进团队内部资源的复用,保持项目间的一致性,提升协作效率并且有助于构建稳定、高效的大型系统。
开发流程
注入SpringBoot的方式
在刚开始开发
Starter
的时候,首先考虑的是怎么能注入到
SpringBoot中
?
这部分涉及到部分
SpringBoot
的自动装配原理,不太清楚的朋友可以补习下;
注入
SpringBoot
需要配置文件,在项目中的
resources
资源目录中创建该目录和文件。
demo-spring-boot-starter
└── src
└── main
└── java
└── com.xbhog
├── DemoBean.java
└── DemoBeanConfig.java
└── resources
└── META-INF
└── spring.factories
在
spring.factories
中我们指定一下自动装配的配置类,格式如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.xbhog.DemoBeanConfig
/**
* @author xbhog
* @describe:
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class DemoBeanConfig {
@Bean
public DemoBean getDemo() {
log.info("已经触发了配置类,正在初始化DemoBean...");
return new DemoBean();
}
}
@Slf4j
public class DemoBean {
public void getDemo(){
log.info("方法调用成功");
}
}
这样就可以将设置的包扫描路径下的相关操作打包到
SpringBoot
中。
SpringBoot
主类启动器:初始化的操作,感兴趣的朋友可以研究下
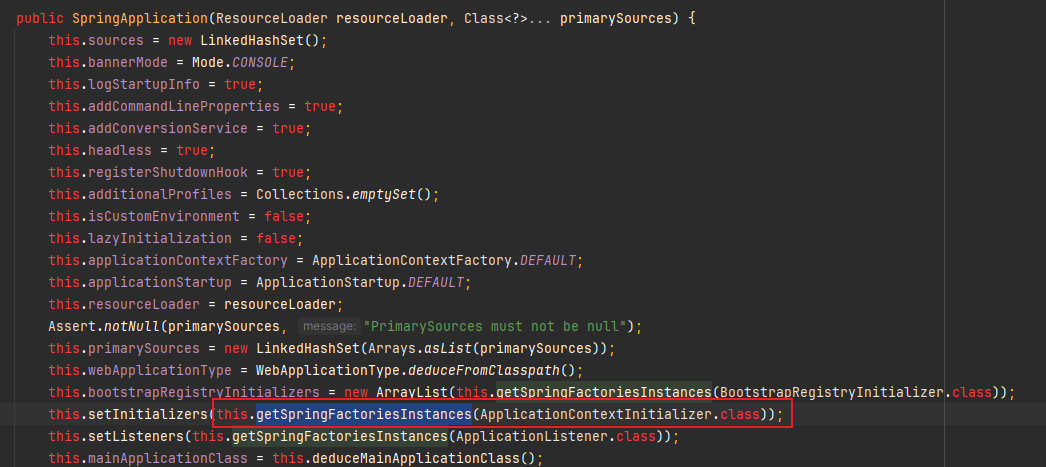

完成后,我们可以打包该项目,然后在测试工程红进行Maven的引入、测试。
测试
新建
Spring
测试工程,引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xbhog</groupId>
<artifactId>demo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
@RestController
public class BasicController implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**两种引入方式都可以
@Autowired
private DemoBean demoBean;*/
@GetMapping("/configTest")
public void configTest() {
DemoBean demoBean = applicationContext.getBean(DemoBean.class);
demoBean.getDemo();
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
请求地址后,可以观察控制台,如下日志表示
SpringBoot Starter
可以使用了。
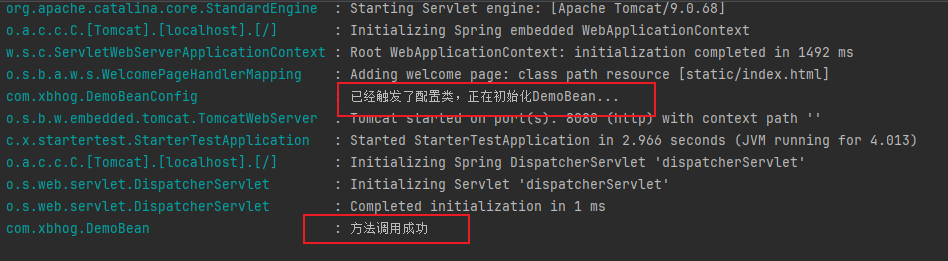
到此,一个简单的
Starter
开发完成了,后续可以围绕工程,根据需求和业务,对通用功能(接口操作日志、异常、加解密、白名单等)进行封装,最后打到
Maven
仓库中进行使用。
自定义SpringBoot Starter(全局加解密)
来源
在之前金融系统开发中,需要对接多个第三方的服务且数据安全性要求比较高;在接口评审阶段需要双方在数据传输的时候进行接口加解密;起初在第一个服务对接的时候,将相关的加解密操作写到工具类中;随着后续服务的增多,代码的侵入越来越严重。
封装
选择通过
Starter
进行功能的封装;好处:引用方便,开发迭代方便,团队复用度高且对业务没有侵入。
开发
思路:通过配置文件初始化,让配置类注解
@ComponentScan
扫描到的
Bean等
注入到
SpringBoot
中,通过自定义注解和``RequestBodyAdvice/ResponseBodyAdvice
组合拦截请求,在
BeforBodyRead/beforeBodyWrite`中进行数据的前置处理,解密后映射到接口接收的字段或对象。
接口上的操作有两种方式:
- 注解+
AOP
实现 - 注解+
RequestBodyAdvice/ResponseBodyAdvice
这里我选择的第二种的
RequestBodyAdvice/ResponseBodyAdvice
,抛砖引玉一下。
【注】
第二种存在的局限性是:只能针对
POST
请求中的
Body
数据处理,无法针对
GET
请求进行处理。
项目结构:
encryAdecry-spring-boot-starter
└── src
└── main
└── java
└── com.xbhog
├── advice
│ ├──ResponseBodyEncryptAdvice.java
│ └──RequestBodyDecryptAdvice.java
├── annotation
│ └──SecuritySupport
├── handler
│ ├──impl
│ │ └──SecurityHandlerImpl.java
│ └──SecurityHandler
└── holder
│ ├──ContextHolder.java
│ ├──EncryAdecryHolder.java
│ └──SpringContextHolder.java
└──GlobalConfig.java
└── resources
└── META-INF
└── spring.factories
项目处理流程图:
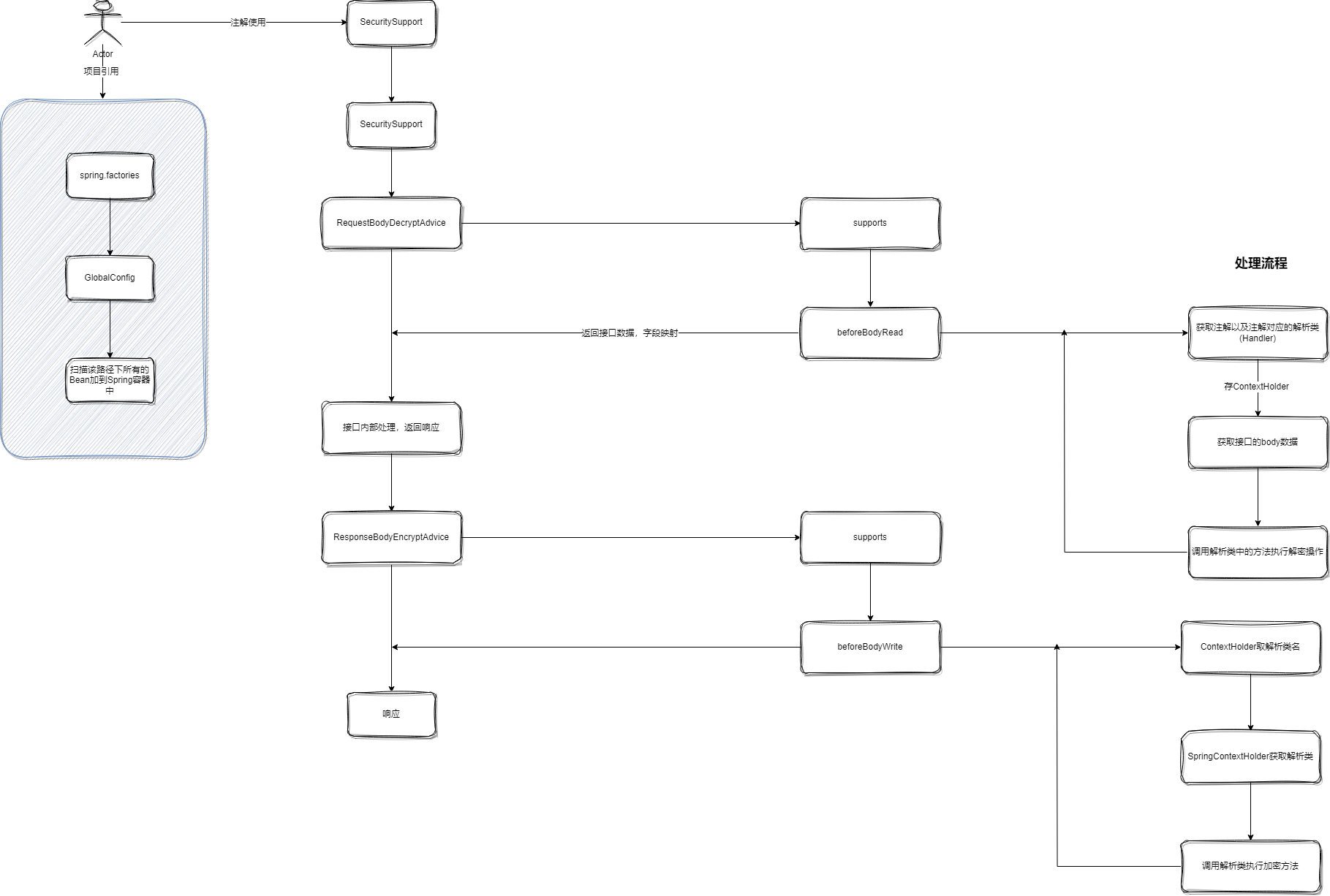
核心代码:
@Override
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException {
log.info("进入【RequestBodyDecryptAdvice】beforeBodyRead的操作,方法:{}",parameter.getMethod());
SecuritySupport securitySupport = parameter.getMethodAnnotation(SecuritySupport.class);
assert securitySupport != null;
ContextHolder.setCryptHolder(securitySupport.securityHandler());
String original = IOUtils.toString(inputMessage.getBody(), Charset.defaultCharset());
//todo
log.info("该流水已插入当前请求流水表");
String handler = securitySupport.securityHandler();
String plainText = original;
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(handler)){
SecurityHandler securityHandler = SpringContextHolder.getBean(handler, SecurityHandler.class);
plainText = securityHandler.decrypt(original);
}
return new MappingJacksonInputMessage(IOUtils.toInputStream(plainText, Charset.defaultCharset()), inputMessage.getHeaders());
}
@Override
public Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
log.info("进入【ResponseBodyEncryptAdvice】beforeBodyWrite的操作,方法:{}",returnType.getMethod());
String cryptHandler = ContextHolder.getCryptHandler();
SecurityHandler securityHandler = SpringContextHolder.getBean(cryptHandler, SecurityHandler.class);
assert body != null;
return securityHandler.encrypt(body.toString());
}
该
Starter
中的全局加解密默认采用的
国密非对称加密SM2
,在开发过程中遇到了该问题
InvalidCipherTextException: invalid cipher text
【原因】 私钥和公钥值不是成对存在的,每次调用
SmUtil.sm2()
会生成不同的随机密钥对。
【解决】在该
Starter
中采用
@PostConstruct
修饰方法,在项目运行中只会初始化运行一次该方法,保证了
SmUtil.sm2()
只会调用一次,不会生成不同的随机秘钥对。
【
ISSUES#1890
】详细请看该地址:
https://hub.fgit.cf/dromara/hutool/issues/1890
/**
* @author xbhog
* @date 2024/02/01 13:23
**/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class EncryAdecryHolder {
public static SM2 sm2 = null;
@PostConstruct
public void encryHolder(){
KeyPair pair = SecureUtil.generateKeyPair("SM2");
byte[] privateKey = pair.getPrivate().getEncoded();
byte[] publicKey = pair.getPublic().getEncoded();
log.info("生成的公钥:{}",publicKey);
log.info("生成的私钥:{}",privateKey);
sm2= SmUtil.sm2(privateKey, publicKey);
}
}
除了默认的加密方式,还可以通过
SecurityHandler
接口进行扩展,扩展出来的
impl
可以在
@SecuritySupport(securityHandler="xxxxxx")
中指定。
/**
* @author xbhog
* @describe: 全局加解密注解
* @date 2023/6/8
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SecuritySupport {
/*securityHandlerImpl*/
String securityHandler() default "securityHandlerImpl";
String exceptionResponse() default "";
}
测试
复用之前的测试项目,引用打包的
mavne
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xbhog</groupId>
<artifactId>encryAdecry-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
启动项目,初始化公私钥。
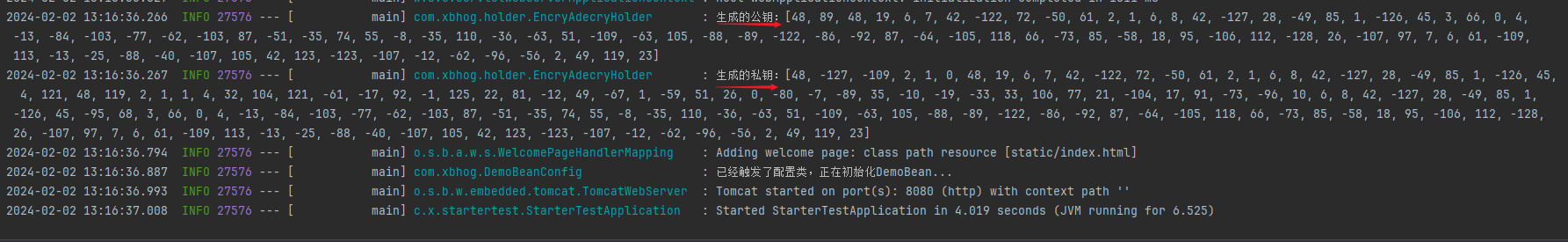

测试接口代码如下:
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class BasicController implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Resource(name = "demoSecurityHandlerImpl")
private SecurityHandler encryAdecry;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
// http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello?name=lisi
//@SecuritySupport(securityHandler = "demoSecurityHandlerImpl")
@SecuritySupport
@PostMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestBody String name) {
return "Hello " + name;
}
@GetMapping("/configTest")
public String configTest(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
/*DemoBean demoBean = applicationContext.getBean(DemoBean.class);
demoBean.getDemo();*/
return encryAdecry.encrypt(name);
//return MD5.create().digestHex16(name);
}
}
优化
优化后的项目结构:
encryAdecry-spring-boot-starter
└── src
└── main
└── java
└── com.xbhog
├── advice
│ ├──ResponseBodyEncryptAdvice.java
│ └──RequestBodyDecryptAdvice.java
├── annotation
│ └──SecuritySupport
├── handler
│ ├──impl
│ │ └──EncryAdecryImpl.java
│ └──SecurityHandler
└── holder
│ ├──ContextHolder.java
│ └──SpringContextHolder.java
├──GlobalProperties.java
└──GlobalConfig.java
└── resources
└── META-INF
└── spring.factories
增加配置类,用于绑定外部配置(
properties
和
YAML
)到Java对象的的一种机制;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(GlobalProperties.PREFIX)
public class GlobalProperties {
/**
* 默认前缀
*/
public static final String PREFIX = "encryption.type";
/**
* 加解密算法
*/
private String algorithmType;
/**
* 加解密key值
*/
private String key;
}
注解修改:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SecuritySupport {
/**
* 项目默认加解密实现类encryAdecryImpl
* */
String securityHandler() default "encryAdecryImpl";
}
重写
Starter
默认的加解密方式:
@Slf4j
@Component
public class EncryAdecryImpl implements SecurityHandler {
@Resource
private GlobalProperties globalProperties;
private static volatile SM2 sm2;
@Override
public String encrypt(String original) {
log.info("【starter】具体加密的数据{}",original);
return sm2.encryptBase64(original, KeyType.PublicKey);
}
@Override
public String decrypt(String original) {
String decryptData = StrUtil.utf8Str(sm2.decryptStr(original, KeyType.PrivateKey));
log.info("【starter】具体解密的数据:{}",decryptData);
return decryptData;
}
@PostConstruct
@Override
public void init() {
log.info("======>获取映射的加密算法类型:{}",globalProperties.getAlgorithmType());
//传的是加密算法
KeyPair pair = SecureUtil.generateKeyPair(globalProperties.getAlgorithmType());
byte[] privateKey = pair.getPrivate().getEncoded();
byte[] publicKey = pair.getPublic().getEncoded();
sm2= SmUtil.sm2(privateKey, publicKey);
}
}