算法 | 迷宫求解
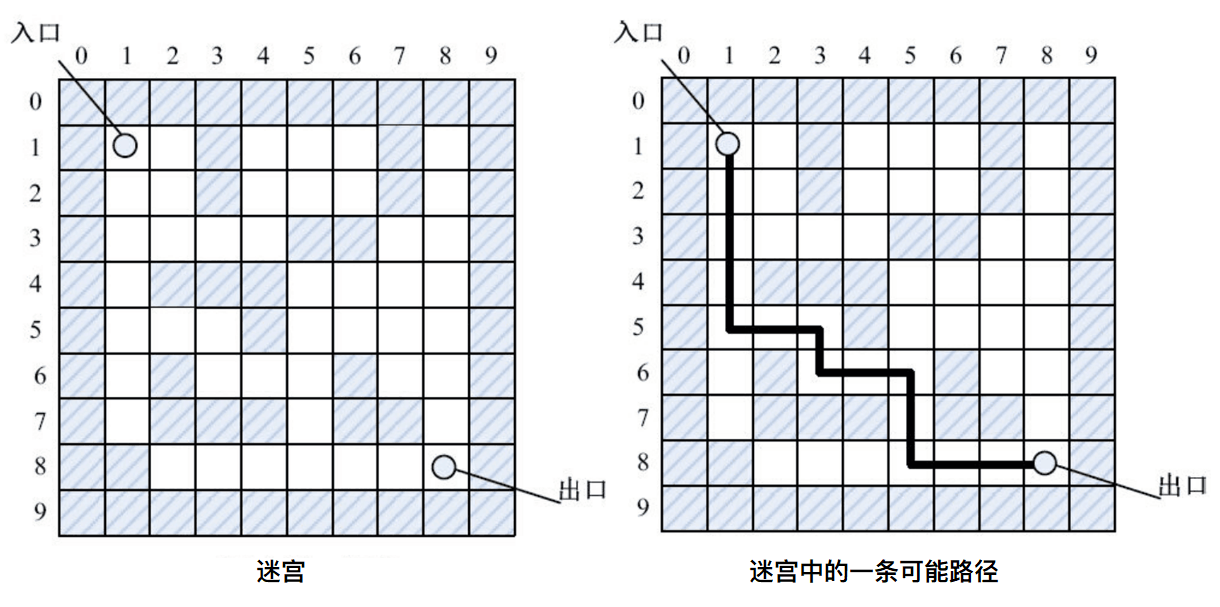
问题描述
参考上图所示迷宫,编写算法求一条从入口到出口的有效路径。
- 图中阴影方块代表墙(不可行走),白色方块代表通道(支持行走)。
- 所求路径必须是简单路径,即所求得的路径上不能重复出现同一通道块。
算法分析
初步分析
通常采用穷举法,即从入口出发,顺某一方向向前探索,若能走通,则继续往前走;否则沿原路返回,换另一个方向继续探索,直到探索到出口为止。
为了保证在任何位置都能原路返回,显然需要用一个先进后出的栈来保存从入口到当前位置的路径。
求迷宫中一条路径的算法的基本思路是:
如果当前位置“可通”,则纳入“当前路径”,并继续朝下一个位置探索,即切换下一个位置为当前位置,如此重复直至到达出口;如果当前位置不可通,则应沿“来向”退回到前一通道块,然后朝“来向”之外的其他方向继续探索;如果该通道块的四周4个方块均不可通,则应从当前路径上删除该通道块。
所谓下一位置指的是当前位置四周(东、南、西、北)4个方向上相邻的方块。
**
具体流程
1.声明一个结构体patch表示每一个方块,含有两个成员:
(1)int type: 1-通道;0-墙;
(2)int flag: 1-未走;0-已走;-1-不可走。
2.创建一个矩阵表示迷宫,元素类型为结构体patch。
3.创建一个栈,用于存储当前路径依次所经过的每个patch的坐标信息(x, y)。
4.从当前位置cur出发(cur初始化为起点位置),然后基于cur按“东-南-西-北”4个方向顺序依次试探,即按选定的试探方向往前进一个patch到达next位置:
(1)若next“可走”,则将cur入栈,同时将cur对应patch的flag更新为0,然后将cur更新为next,然后重复4;
(2)若next“不可走”,则改变试探方向基于cur前进一个patch获取新next,然后重复(1);
(3)若cur的“东-南-西-北”4个方向均“不可走”,则代表当前位置cur对应patch不可通,将cur对应patch的flag设为-1,执行出栈操作,并将cur更新为出栈元素对应的位置,将新cur对应patch的flag更新为1,然后重复4。
(4)若next等于终点,则将cur和next均入栈并将二者对应patch的flag更新为0,寻找有效路径结束。
(5)寻找过程中,若当前位置cur重新回退至起点位置,代表所给迷宫无解。
5.栈内存储的从“栈底元素 - 栈顶元素”对应的patch序列即为有效路径。
代码实现
step1 : 结构体定义与创建
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxMazeSize 40 /* 迷宫的最大行列*/
#define MaxStackSize 100 /*栈的最大容量*/
/*声明一个结构体表示patch的坐标信息*/
typedef struct
{
int x, y;
} Position;
/* 声明一个结构体patch表示每一个方块 */
typedef struct
{
int type = 0; // 0-墙;1-通道
int flag = 1; // 0-已走;1-未走(可走);-1-不可走(禁走)
} Patch;
/*声明栈结构体*/
typedef struct
{
Position data[MaxStackSize];
Position *top = data; // 默认初始化栈
} PosStack;
PosStack S; // 创建栈保存有效路径坐标信息
Patch maze[MaxMazeSize][MaxMazeSize]; // 创建迷宫(二维列表):元素类型为结构体patch
int rows, cols; // 迷宫的行数及列数
Position startPos, endPos; // 起点坐标 + 终点坐标
step2 : 迷宫初始化
/*初始化迷宫*/
void InitMaze()
{
int walls;
cout << "Please enter the number of rows and columns in the maze (separated by spaces): ";
cin >> rows >> cols;
int k = 0;
while (k < cols) // 设置迷宫外墙
{
maze[0][k].type = 0;
maze[0][k].flag = -1;
maze[rows - 1][k].type = 0;
maze[rows - 1][k].flag = -1;
k++;
}
k = 0;
while (k < rows) // // 设置迷宫外墙
{
maze[k][0].type = 0;
maze[k][0].flag = -1;
maze[k][cols - 1].type = 0;
maze[k][cols - 1].flag = -1;
k++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++) // 内部区域全部初始化为通道
{
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; j++)
{
maze[i][j].type = 1;
maze[i][j].flag = 1;
}
}
cout << "Please enter the number of walls in the maze: ";
cin >> walls; // 用户自定义设置内部区域墙的数量
cout << "Enter the coordinates of each wall (x and y are separated by spaces):\n";
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < walls; i++) // 用户自定义设置内部区域墙的位置
{
cin >> x >> y;
maze[x][y].type = 0;
maze[x][y].flag = -1;
}
}
step3 : 展示迷宫
/*展示迷宫结构*/
void DisplayMaze(int rows, int cols)
{
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
{
cout << "\t" << maze[i][j].type;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
step4 : 判断某个位置对应的方块是否可走
/*给定坐标,判断该坐标对应patch是否可走*/
bool JudgeNext(Position next)
{
if (next.x < 0 && next.y > rows - 1)
{ // 判断该坐标是否越界
return false;
}
if (maze[next.y][next.x].type == 0)
{ // 判断该坐标对应patch是墙还是通道
return false;
}
if (maze[next.y][next.x].flag <= 0)
{ // 判断该坐标对应patch是否可走
return false;
}
return true;
}
step5 : 迷宫求解-寻找有效路径
/*迷宫求解*/
bool FindMazePath()
{
bool reFlag = false;
Position curPos = startPos; // 当前位置
Position nextPos; // 下一试探位置
int direction;
while (1)
{
direction = 1;
while (direction <= 4)
{
if (direction == 1) // 东
{
nextPos.x = curPos.x + 1;
nextPos.y = curPos.y;
}
else if (direction == 2) // 南
{
nextPos.x = curPos.x;
nextPos.y = curPos.y + 1;
}
else if (direction == 3) // 西
{
nextPos.x = curPos.x - 1;
nextPos.y = curPos.y;
}
else // 北
{
nextPos.x = curPos.x;
nextPos.y = curPos.y - 1;
}
if((nextPos.x == endPos.x) && (nextPos.y == endPos.y)){ // 抵达终点
*(S.top++) = curPos;
*(S.top++) = nextPos;
maze[curPos.y][curPos.x].flag = 0;
maze[nextPos.y][nextPos.x].flag = 0;
reFlag = true;
break;
}
if (JudgeNext(nextPos)){
break;
}else{
direction++; // 准备尝试下一试探方向
}
}
if (direction > 4) // 当前位置不可通
{
maze[curPos.y][curPos.x].flag = -1;
curPos = *(--S.top); // 执行出栈操作,并将当前位置更新为出栈patch对应位置
maze[curPos.y][curPos.x].flag = 1;
}else{ // next可走
*(S.top++) = curPos;
maze[curPos.y][curPos.x].flag = 0;
curPos = nextPos;
}
if(reFlag){
break; // 抵达终点,找到有效路径,终止寻找
}
if((curPos.x == startPos.x) && (curPos.y == startPos.y)){
cout << "Maze without a solution!\n";
break;
}
}
return reFlag;
}
step6 : 主方法调用
int main()
{
InitMaze();
cout << "The maze is structured as follows:\n";
DisplayMaze(rows, cols);
cout << "Please enter the coordinates of the starting point (x and y are separated by spaces): ";
cin >> startPos.x >> startPos.y;
cout << "Please enter the coordinates of the end point (x and y are separated by spaces): ";
cin >> endPos.x >> endPos.y;
if(FindMazePath()){
cout << "Successfully found an effective path, as shown below:\n";
int length = S.top - S.data;
Position tmp;
for(int i = 0; i< length; i++){
tmp = *(--S.top);
maze[tmp.y][tmp.x].type = length - i;
}
DisplayMaze(rows, cols);
}else{
cout << "Failed to find a effective path!\n";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
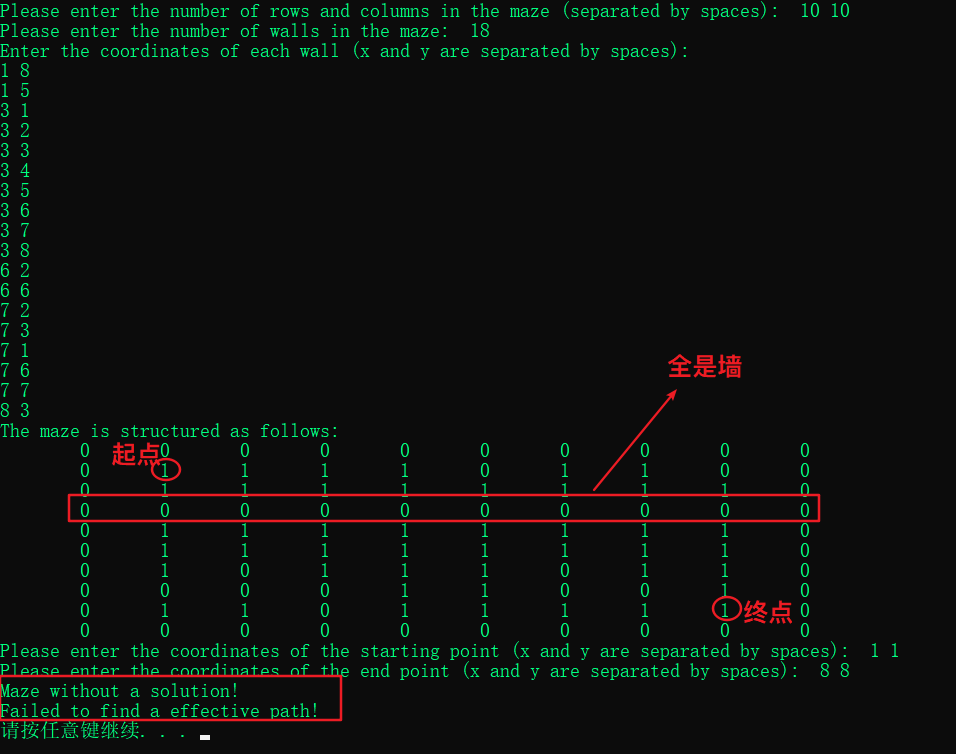
运行效果
case1 : 迷宫有解
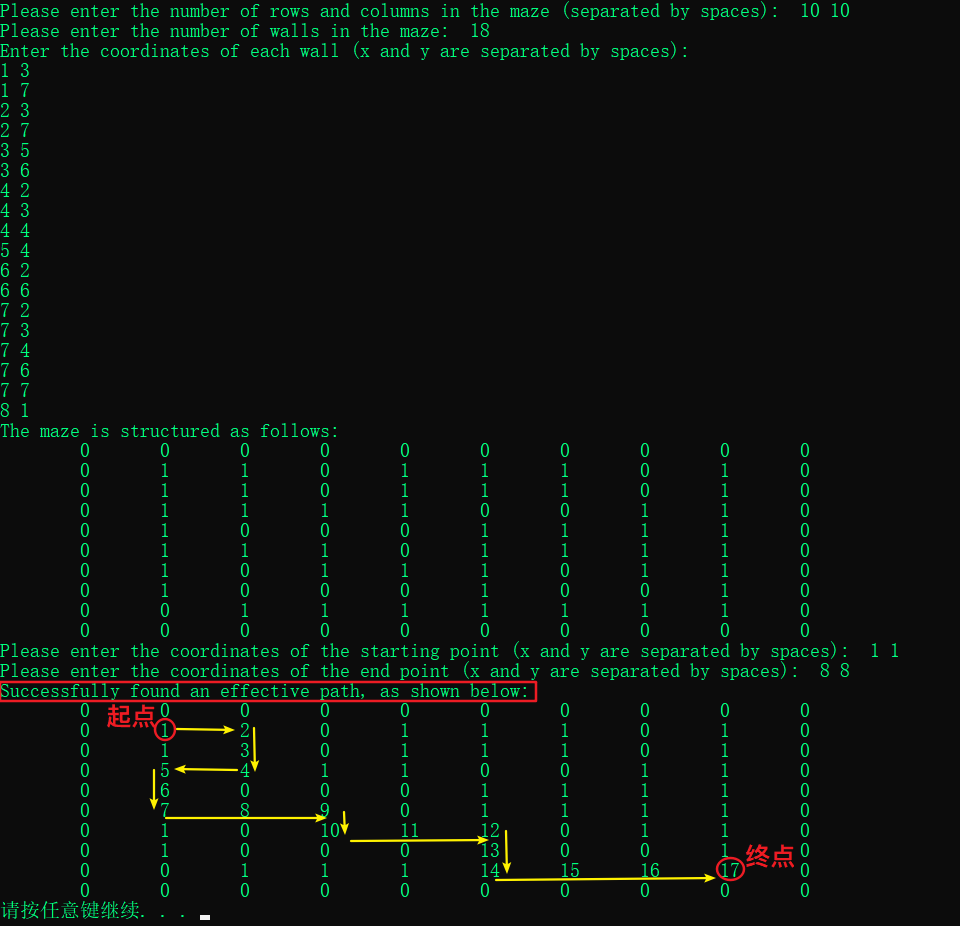
case2 : 迷宫无解