c# 异步进阶———— paralel [二]
前言
简单整理一下paralel,以上是并行的意思。
正文
我们在工作中常常使用task await 和 async,也就是将线程池进行了封装,那么还有一些更高级的应用。
是对task的封装,那么来看下paralel。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var ints= Enumerable.Range(1, 100);
var result = Parallel.ForEach(ints, arg =>
{
Console.WriteLine(arg);
});
Console.Read();
}
可以看到结果是并行的。

那么来看下实现机制。
public static ParallelLoopResult ForEach<TSource>(IEnumerable<TSource> source, Action<TSource> body)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(source));
}
if (body == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(body));
}
return ForEachWorker<TSource, object>(
source, s_defaultParallelOptions, body, null, null, null, null, null, null);
}
进行参数检验,然后交给了ForEachWorker。
这是一个基本的代码思路,就是复杂的方法中可以先校验参数,然后具体实现交给另外一个方法。
然后通过不同的类型,进行分类:
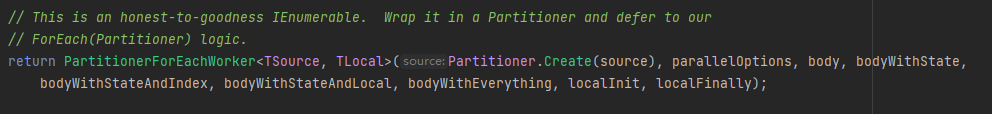
然后看下具体实现是什么?
进去看就是一个taskreplicator:

看下run在做什么。
public static void Run<TState>(ReplicatableUserAction<TState> action, ParallelOptions options, bool stopOnFirstFailure)
{
int maxConcurrencyLevel = (options.EffectiveMaxConcurrencyLevel > 0) ? options.EffectiveMaxConcurrencyLevel : int.MaxValue;
TaskReplicator replicator = new TaskReplicator(options, stopOnFirstFailure);
new Replica<TState>(replicator, maxConcurrencyLevel, CooperativeMultitaskingTaskTimeout_RootTask, action).Start();
Replica nextReplica;
while (replicator._pendingReplicas.TryDequeue(out nextReplica))
nextReplica.Wait();
if (replicator._exceptions != null)
throw new AggregateException(replicator._exceptions);
}
创建了一个taskreplictor,起到管理作用
然后创建了一个Replica,然后这个start 是关键
然后通过while,让每一个Replica 都运行完毕才推出,达到同步的效果
if (replicator._exceptions != null)
throw new AggregateException(replicator._exceptions);
可以看一下这个,这个是一个比较好的技巧。如果一个运行管理,不用抛出异常,之间在管理中进行运行处理总结。
比如结果,异常等。
那么就看下这个start。
protected Replica(TaskReplicator replicator, int maxConcurrency, int timeout)
{
_replicator = replicator;
_timeout = timeout;
_remainingConcurrency = maxConcurrency - 1;
_pendingTask = new Task(s => ((Replica)s).Execute(), this);
_replicator._pendingReplicas.Enqueue(this);
}
public void Start()
{
_pendingTask.RunSynchronously(_replicator._scheduler);
}
将会运行Execute,是同步的,而不是异步的,也就是说第一个task将会运行在当前线程。
那么看Execute在做什么?
public void Execute()
{
try
{
if (!_replicator._stopReplicating && _remainingConcurrency > 0)
{
CreateNewReplica();
_remainingConcurrency = 0; // new replica is responsible for adding concurrency from now on.
}
bool userActionYieldedBeforeCompletion;
ExecuteAction(out userActionYieldedBeforeCompletion);
if (userActionYieldedBeforeCompletion)
{
_pendingTask = new Task(s => ((Replica)s).Execute(), this, CancellationToken.None, TaskCreationOptions.None);
_pendingTask.Start(_replicator._scheduler);
}
else
{
_replicator._stopReplicating = true;
_pendingTask = null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
LazyInitializer.EnsureInitialized(ref _replicator._exceptions).Enqueue(ex);
if (_replicator._stopOnFirstFailure)
_replicator._stopReplicating = true;
_pendingTask = null;
}
}
一段一段分析:
if (!_replicator._stopReplicating && _remainingConcurrency > 0)
{
CreateNewReplica();
_remainingConcurrency = 0; // new replica is responsible for adding concurrency from now on.
}
这里当_replicator 也就是任务复制器没有停止的时候。这里有两种情况会停止,一种是任务完成,一种是任务异常且设置参数异常时候停止。
_remainingConcurrency 指的是副本数,默认是int.max。
那么就复制一个副本。
protected override void CreateNewReplica()
{
Replica<TState> newReplica = new Replica<TState>(_replicator, _remainingConcurrency, GenerateCooperativeMultitaskingTaskTimeout(), _action);
newReplica._pendingTask.Start(_replicator._scheduler);
}
复制完副本后,那么就开始运行我们的action了。
protected override void ExecuteAction(out bool yieldedBeforeCompletion)
{
_action(ref _state, _timeout, out yieldedBeforeCompletion);
}
这里传入了timeout,这个timeout并不是我们限制我们单个task的运行时间,而是当运行到一定时候后,这个task就停止运行,然后另外启动一个副本。
if (CheckTimeoutReached(loopTimeout))
{
replicationDelegateYieldedBeforeCompletion = true;
break;
}
if (userActionYieldedBeforeCompletion)
{
_pendingTask = new Task(s => ((Replica)s).Execute(), this, CancellationToken.None, TaskCreationOptions.None);
_pendingTask.Start(_replicator._scheduler);
}
else
{
_replicator._stopReplicating = true;
_pendingTask = null;
}
这个是为了符合操作系统的调度思想,跑的越久的,基本上优先级会低些。
那么看下这个_action主要在做什么吧。
while (myPartition.MoveNext())
{
KeyValuePair<long, TSource> kvp = myPartition.Current;
long index = kvp.Key;
TSource value = kvp.Value;
// Update our iteration index
if (state != null) state.CurrentIteration = index;
if (simpleBody != null)
simpleBody(value);
else if (bodyWithState != null)
bodyWithState(value, state);
else if (bodyWithStateAndIndex != null)
bodyWithStateAndIndex(value, state, index);
else if (bodyWithStateAndLocal != null)
localValue = bodyWithStateAndLocal(value, state, localValue);
else
localValue = bodyWithEverything(value, state, index, localValue);
if (sharedPStateFlags.ShouldExitLoop(index)) break;
// Cooperative multitasking:
// Check if allowed loop time is exceeded, if so save current state and return.
// The task replicator will queue up a replacement task. Note that we don't do this on the root task.
if (CheckTimeoutReached(loopTimeout))
{
replicationDelegateYieldedBeforeCompletion = true;
break;
}
}
就是拉取我们的enumerator的数据,然后simpleBody(value),进行运行我们写的action。
总结一下,其实Parallel 核心就是一个任务复制器,然后创建多个副本,拉取我们的数据,进行执行我们设置的action。
里面的主要功能,Parallel做到了限制副本数,因为我们知道task并不是越多越好。
第二个,如果长时间运行,那么Parallel是做了优化的,当达到timeout的时候,那么会重新启动一个副本(可以理解为一个线程)
第三点,Parallel 有一个foreach 进行迭代器的处理,这里不仅仅是让任务可以并行。
而且具备c# foreach的基本功能。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var ints= Enumerable.Range(1, 100);
var result = Parallel.ForEach(ints, (arg, state)
=>
{
if (state.IsStopped)
{
return;
}
if (arg > 18)
{
state.Break();
}
});
if (result.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine("完成");
}
Console.Read();
}
可以进行中断。
还有一个函数,那就是stop,这个stop 比break 停止的快,break 要记录出,最小中断位置。
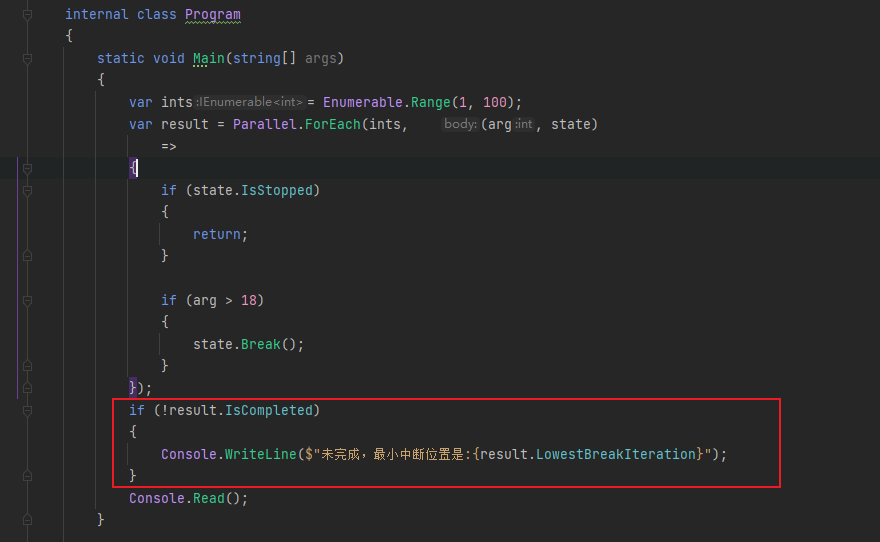
而stop 就是立马停止下来。
结
在上述中,我们知道可以传递一个taskschedule进行,那么这个taskschedule 是干什么的,对我们的任务调度有什么影响呢? 下一节,自我实现taskschedule。